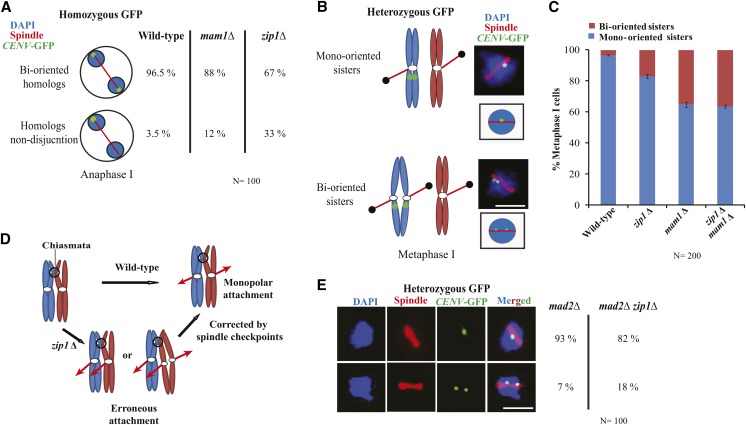
Figure 3.
The absence of Zip1 causes homologs non-disjunction and sister chromatid bi-orientation during meiosis I. (A) Immunofluorescence assay is showing the percentage of anaphase I cells of wild-type (SGY116), mam1Δ (SGY223) and zip1Δ (SGY1127) with homologs disjunction or non-disjunction. Around 100 cells were analyzed for each strain. (B) Schematic of mono or bi-orientation of sister chromatids along with the representative images during metaphase I (C) Immunofluorescence analysis showing the percentage of wild-type (SGY115), mam1Δ (SGY220), zip1Δ (SGY1427) and mam1Δ zip1Δ (SGY3190) cells at metaphase I with mono- or bi-oriented sister chromatids. The cells were counted from two independent experiments for each strain and the total number of cells are represented as N. (D) Schematic showing monopolar attachment of the sister chromatids during metaphase I and possible correction of erroneous attachment by spindle checkpoint proteins. (E) The mono-oriented and bi-oriented sisters were counted similarly as described in ‘B’ using mad2Δ (SGY1265) and zip1Δ mad2Δ (SGY1267) cells. Around 100 cells were observed for each strain. Bar, ∼5 µm. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean.