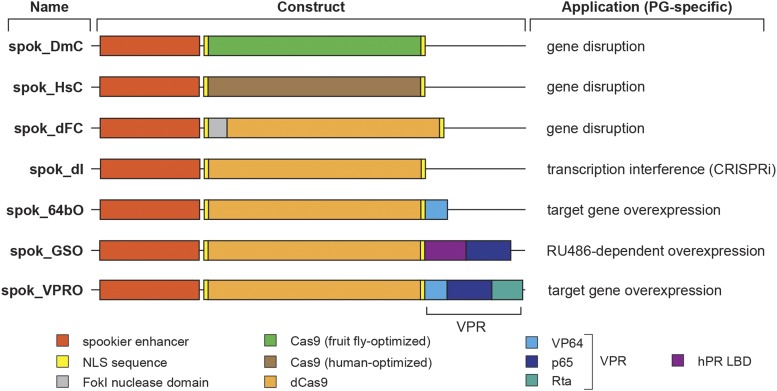
Figure 3.
The PG-specific Cas9 (PG-Cas9) vector collection. All vectors are based on the general Gateway Cas9 vector collection (Figure S2). Each PG-Cas9 vector backbone (not shown) is composed of a mini-white gene as a marker, a PhiC31 integrase-compatible attB site, the bla coding sequence to mediate ampicillin resistance, and a synthetic core promoter. Shown here are the spookier (spok) regulatory region, the Cas9 variant, the regions encoding Nuclear Localization Sequences (NLS), activations domains (VP64, p65 and Rta), the human Progesterone Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain (hPR LBD) and the FokI nuclease domain. spok_DmC, spok_HsC and spok_dFC can be used to generate somatic mutations (C = cleavage). spok_DmC uses a fruit fly codon-optimized Cas9 version, while spok_HsC is optimized for human cells. spok_dFC cuts DNA upon FokI-mediated dimerization followed by FokI cleavage, since dCas (= dead Cas9) is unable to cut DNA. However, the spok_dI (I = interference) vector harbors dCas9 and can be used to interfere with transcription (CRISPRi) by guiding Cas9 into the vicinity of transcriptional start sites where it may block the assembly of the pre-initiation complex. spok_64bO, spok_GSO and spok_VPRO (O = overexpression)were designed to achieve upregulation of target genes. spok_GSO (GeneSwitch activation) encodes a protein where Cas9 is fused to the hPR LBD and p65 domain, allowing activation via RU486.