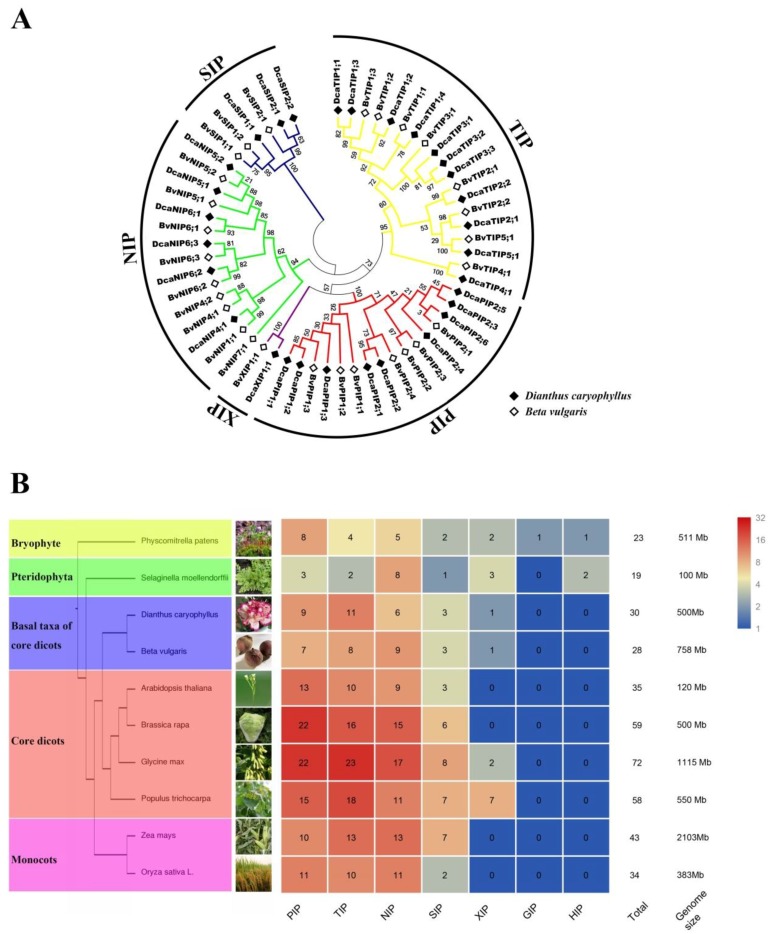
Figure 1.
(A) Phylogenetic tree from DcaAQPs and B. vulgaris L. Multiple alignments were conducted by Clustal W and phylogenetic tree was generated by MEGA 6.0 using Maximum Likelihood (ML) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The different subfamilies were indicted by a circle and different colors; (B) The distribution of AQPs among different species was compared based on previous report (Deshmukh et al. 2016; Sonah et al. 2017). Schematic of species phylogenetic relationships was built by EvolView (https://www.plob.org/tag/evolview), and the number of AQPs was shown by heat map using R software.