Table 1.
Examples of lipid classes and representative molecules. PE—Phosphatidylethanolamine; PC—Phosphatidylcholine; TG—Triacylglycerol; WE—Wax ester.
| Lipids | Example | Role | Specificities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty acids |
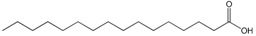 16:0 |
Building blocks for numerous lipids, regulation of membrane fluidity | - |
| Glycerophospholipids or phospholipids |
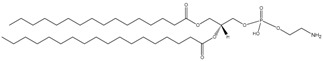 PE (16:0/18:0) |
Main constituent of cellular membranes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes | Two FA linked to a glycerol molecule connected to a phosphate head group |
| Glycerophospholipids plasmalogens |
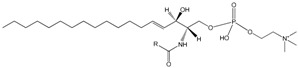 Sphingomyelin |
Organization and stability of membranes; cellular signalling | Contain a vinyl-ether and an ester bond at the glycerol backbone |
| Glycerophospholipids sphingolipids | Sphingomyelin | Role in cell division, differentiation and cell death | Long-chain or sphingoid base linked to a FA via an amide bond |
| Glycerolipids |
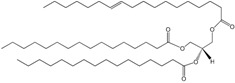 TG (16:0/16:0/18:1) |
Storage compounds in prokaryotes | Mono-, di-, or tri-substituted glycerols |
| Ether-linked lipids such as glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers |
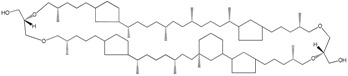 Crenarchaeol |
Core cellular membrane lipids in many archaea | Isoprenoid moieties linked by ether bonds to glycerol |
| Wax esters |
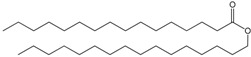 WE(16:0/16:0) |
Energy storage and cell structure | Ester of FA and a fatty alcohol |
| Sterol lipids |
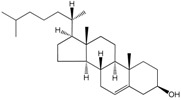 Cholesterol |
Maintenance of membrane fluidity | Steroids with a hydroxyl group at the 3-position of the A-ring |
