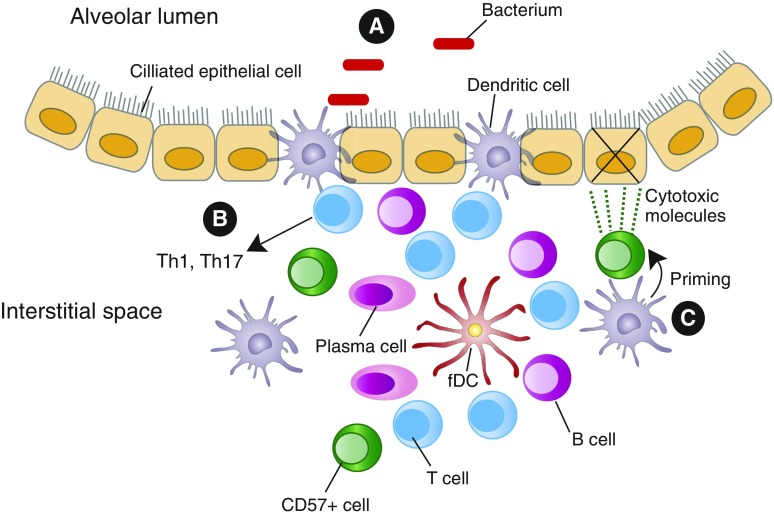
Figure 2.
Lung DCs in LLF. Lung DCs can contribute to the formation of LLF. In addition to draining lymph nodes, LLF provide a microenvironment where DCs interact with other cells. (A) Antigen uptake may also be occurring in LLF, where many DCs, including CD103+/Langerin+ DCs, directly interface with the alveolar spaces (52). (B) CD103+ DCs drive Th1 and Th17 responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, whereas IL-17 production can initiate development of new LLF. (C) Signals from DCs could prime CD57+ NK cells to become cytotoxic and kill epithelial cells. CD, cluster of differentiation; fDC, follicular DCs; LLF, lung lymphoid follicles; NK, natural killer; Th, T helper cell.