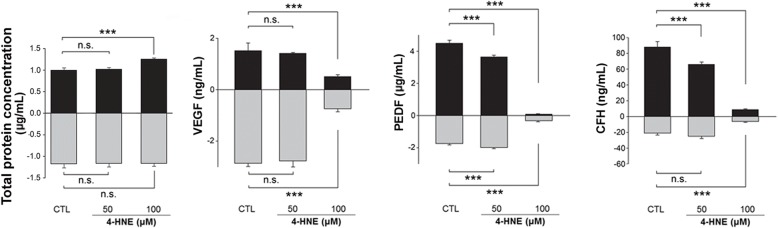
Fig. 6.
Differential secretion of selected proteins in hfRPE cell cultures. Total protein concentrations in conditioned media from apical and basal baths (left end). To confirm the biological activity of VEGF, PEDF, and CFH, apical or basal media were collected at 24 h and then analyzed using ELISAs (the rest three graphs). The amount of VEGF protein in the basal media was higher than that in the apical media (2.86 ng/mL vs. 1.51 ng/mL) and was greatly decreased by 100 μM 4-HNE treatment (0.74 ng/mL vs. 0.51 ng/mL). PEDF secretion on the apical side was higher than that on the basal side (4.51 μg/mL vs. 1.74 μg/mL), and the level of PEDF was significantly decreased in a dose-dependent manner at 24 h (0.086 μg/mL and 0.32 μg/mL, in apical and basal baths treated with 100 μM 4-HNE). The ratio of the PEDF concentrations secreted in the apical and basal chambers was reversed in cultures treated with 100 μM 4-HNE. The apical/basal ratios were 2.59 and 1.83 in control cultures and cultures exposed to 50 μM 4-HNE for 24 h; the apical/basal ratio was 0.27 in cultures exposed to 100 μM 4-HNE for 24 h. The level of CFH showed similar changes: it decreased both apically and basally in cultures exposed to oxidative stress compared to control cultures. The apical/basal ratios were 4.19 and 2.64 in control cultures and cultures exposed to 50 μM 4-HNE for 24 h, respectively; the apical/basal ratio was 1.41 in cultures exposed to 100 μM 4-HNE for 24 h