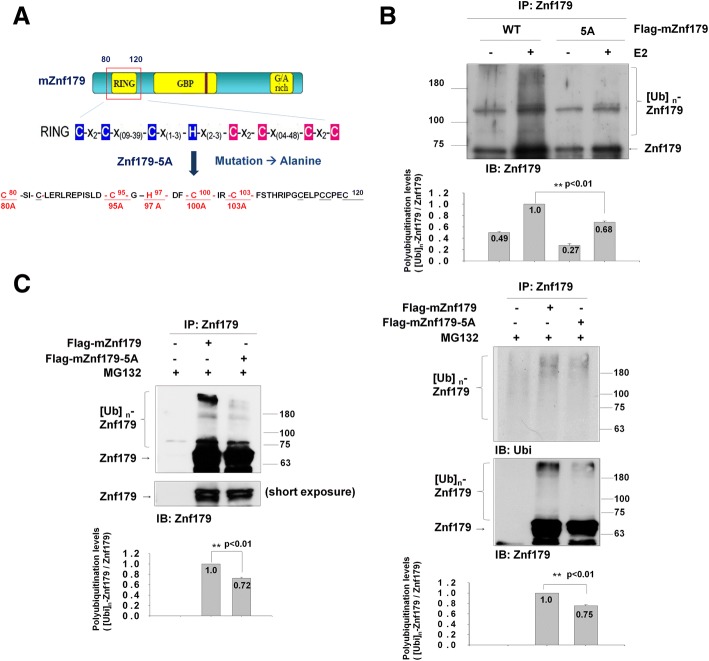
Fig. 2.
Autoubiquitination of Znf179-5A mutant is decreased in vitro and in vivo. a A schematic diagram of the Znf179-5A mutants is shown. Several point mutations (C80A, C95A, H97A, C100A, C103A) were generated within the C3HC4 motif on the RING domain of Znf179 to create the Znf179-5A mutant. b 293 T cells were transfected with Flag-mZnf179 or Flag-mZnf179-5A mutant for 48 h. The immunoprecipitated Flag-mZnf179 or Flag-mZnf179-5A proteins were introduced to the mixture of purified E1, ubiquitin, Mg2+-ATP and purified His-UbcH5c E2 enzymes to perform in vitro ubiquitination assays. The ubiquitination patterns of Znf179 and its immunoprecipitation levels were detected in parallel by Western blotting with anti-ubiquitin and anti-Znf179 antibodies. c and d Cell lysates from N2a cells (c); or 293 T cells (d) expressing Flag-mZnf179 and Flag-mZnf179-5A mutant were immunoprecipitated with anti-Znf179 antibody and analyzed with anti-ubiquitin and anti-Znf179 antibodies by Western blotting. b-d Data were presented as the mean ± SEM (006E = 3) of at least three independent experiments (** p < 0.01, groups were compared by t-test, two-tailed p values). The polyubiquitination levels are compared between [Ubi]n-Flag-mZnf179/Flag-mZnf179 and [Ubi]n-Flag-mZnf179-5A/Flag-mZnf179-5A