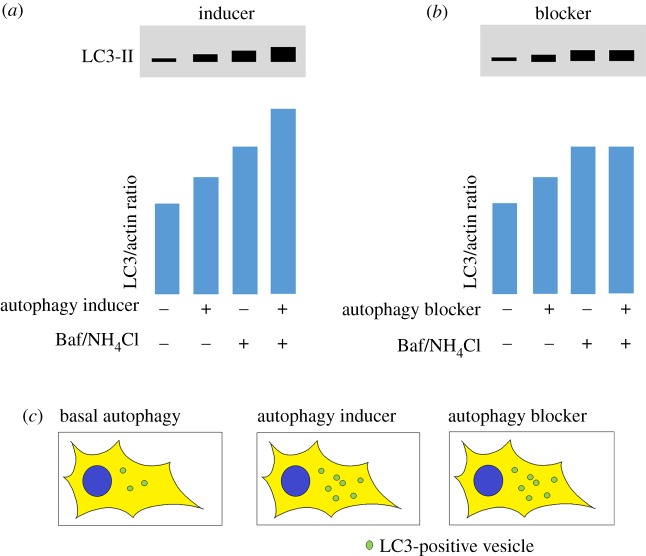
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of conventional methods to measure rates of autophagy. (a,b) Western blots for LC3-II: Measuring LC3 lipidation by western blotting is one of the best-established methods for measuring autophagic flux. However, care must be taken in interpreting increases in LC3 levels as this may occur as a result of an increase in autophagosome formation (upregulation) or a blockage in clearance. To discriminate between these two scenarios, assays should be performed in basal conditions and in the presence of an agent that prevents lysosomal degradation such as bafilomycin A1 (Baf) or ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). (a) When autophagy is induced, LC3-II levels increase as more autophagosomes are formed. In the presence of a lysosomal blocker, LC3-II levels increase further because increased autophagosome formation still occurs, but autophagosomes cannot be cleared and therefore build up within the cell. (b) In some conditions when autophagy is blocked (for example, if fusion with the lysosome is prevented), LC3-II levels can also increase because autophagosomes may form but are not degraded. In this scenario, when LC3-II levels are measured in the presence of Baf or NH4Cl, LC3-II levels are unchanged. The difference in patterns between (a) and (b) can be used to discriminate between autophagy induction and blockage. (c) When LC3-labelled vesicles (puncta) are measured within cells with a single fluorophore (e.g. cells expressing GFP-tagged LC3 or immunofluorescence labelling of the endogenous protein), an increase in puncta can be observed both in autophagy inducing and autophagy blockage conditions. N.B. Commercially available antibodies with cross-reactivity to zebrafish LC3 are widely available from suppliers such as from Novus Biologicals (used in [7–9]) and Cell Signaling Technology (used in [10]).