Fig. 4.
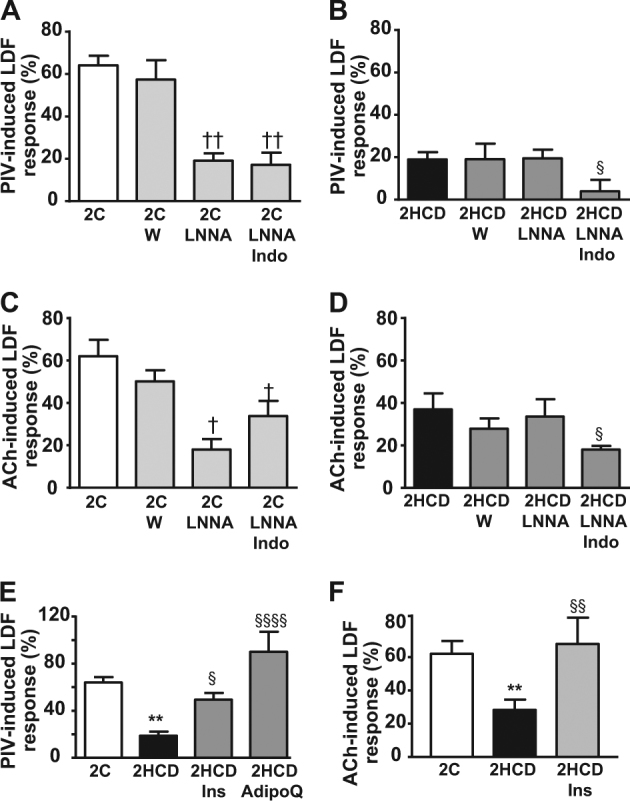
Mechanisms involved in impaired PIV and Ach responsiveness in overweight metabolically healthy mice. Mice were fed either a standard chow (C; white or light grey bars) or hypercaloric diet (HCD; black or dark grey bars) for 2 weeks. Effects of selected pharmacological inhibitors were determined on microvascular response to local pressure application (a, b) or Ach stimulation (c, d). Inhibitors included PI3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin (W; n = 10), nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, L-NG-nitro-L-arginine (LNNA; n = 10) and LNNA + anti-inflammatory COX-1/2 inhibitor, indomethacin (LNNA + Indo; n = 5). e Effects in vivo administration of insulin (Ins; n = 10) and adiponectin (AdipoQ; n = 9) on impaired PIV response in 2-week-HCD fed mice. f Effects in vivo administration of insulin (Ins; n = 6) on impaired Ach-induced response in 2-week-HCD fed mice. Data represents mean ± SEM. †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 vs. 2-week-C diet fed mice; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. age-matched control diet fed mice; and §p < 0.05, §§p < 0.001, §§§§p < 0.00001 vs. 2-week hypercaloric diet fed mice
