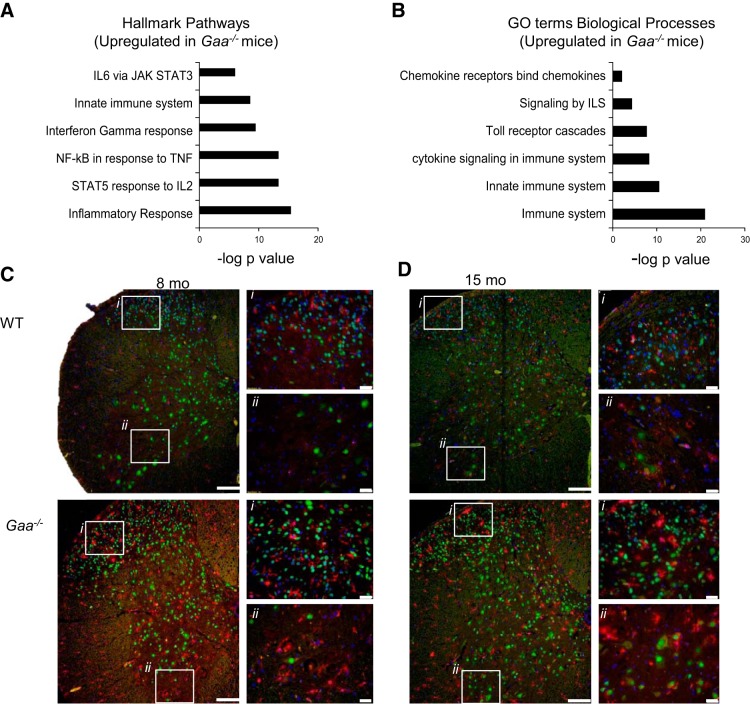
Fig. 5.
Proinflammatory signaling and ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA-1) staining indicate neuroinflammation in Gaa−/− cervical spinal cord. Analysis of upregulated Hallmark signaling pathways (FDR q value <0.05; A) and Gene Ontology (GO) terms biological processes (FDR q value <0.05; B) showed clear increases in proinflammatory signaling in Gaa−/− compared with WT tissues. Enriched signaling pathway data are expressed as the negative log10 of the P value. Histological examination showed no signs of “activated” microglia in WT tissues. However, in Gaa−/− tissues, there were multiple examples of IBA-1-positive microglia with a “bushy” appearance, an amoeboid morphology, or colocalization with neurons at 6–8 mo (C) and 12–15 mo age points (D). In C and D, i indicates the dorsal horn region and ii indicates the ventral horn region. Calibration bars indicate 100 μM (lower-power images) and 20 μM (higher-power images). IBA-1 staining is shown in red, NeuN is shown in green, and DAPI is in blue.