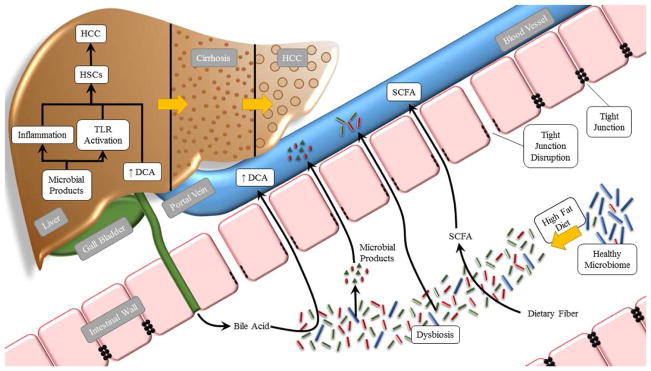
Fig. 2. Effects of the intestinal microbiota on HCC tumorigenesis.
Long term ingestion of a HFD results in dysbiosis and intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Greater intestinal permeability leads to translocation of microbial products to the liver and causes inflammation and TLR activation, which can stimulate HSCs to produce pro-fibrotic factors, In addition, changes in the gut microbiota can result in higher levels of DCA, which provoke a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in HSCs. All of these factors promote the development of HCCs. Abbreviations: HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HFD, high fat diet; TLR, Toll-like recepter; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; DCA, deoxycholic acid; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid.