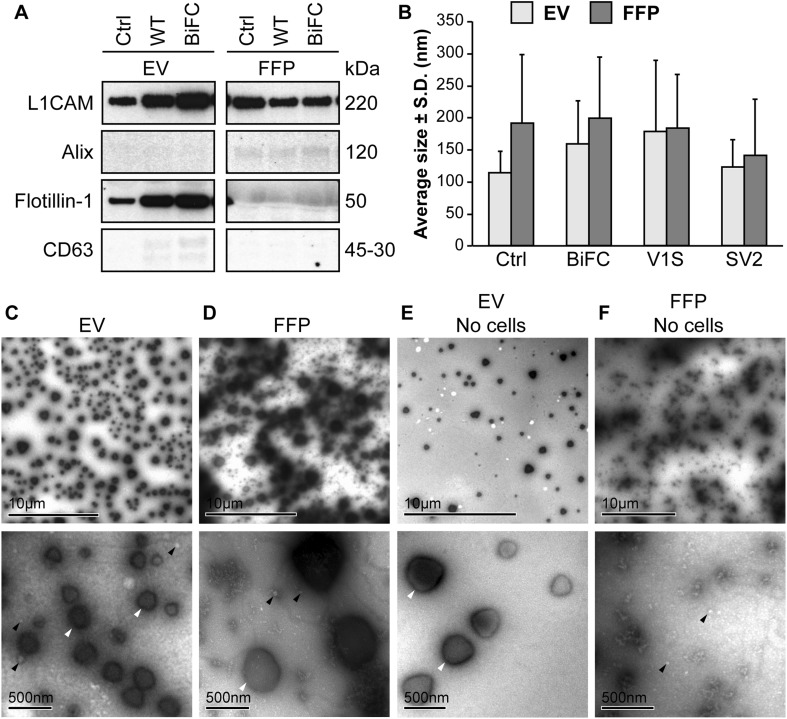
Fig. 2.
The EV fractions are enriched in exosomal markers. a Western blots of the lysed EVs and the corresponding FFP fractions were analyzed for presence of the markers L1CAM, Alix, Flotillin-1, and CD63. Flotillin-1 was the only marker that was highly enriched in all the EV fractions compared to the FFP fractions, but also CD63 was slightly enriched in EVs, indicating that different markers may be differentially present in different subclasses of EVs. The membrane images have been cut to exclude samples outside the scope of this project. Unbiased contrast changes have been made to the images, but the unchanged, whole membrane is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. b NanoSight analysis of EVs and FFP fractions showed similarly sized particles in samples from non-transfected (Ctrl) and tagged α-syn transfected cells with an average diameter of approximately 150 nm. The FFP fraction also contained particles of a similar size, albeit to a much lesser degree than the EV fraction. c TEM analysis of the EV-enriched fraction displayed EVs with diameters between 50 and 500 nm. Both large high density (white arrowheads) and small less dense (black arrowheads) particles were highly enriched. d TEM analysis confirmed the NanoSight results, where small EVs (white arrowheads) and large, dense particles (black arrowhead) were found in the FFP fraction. e Ultracentrifuged growth medium containing EV-depleted FBS also displayed the large particles in the EV fraction (white arrowheads), albeit to a much lesser degree than the EV fraction. f A few small EVs (black arrowheads), but no large vesicles, were found in the FFP after ultracentrifugation of the FBS-depleted growth medium