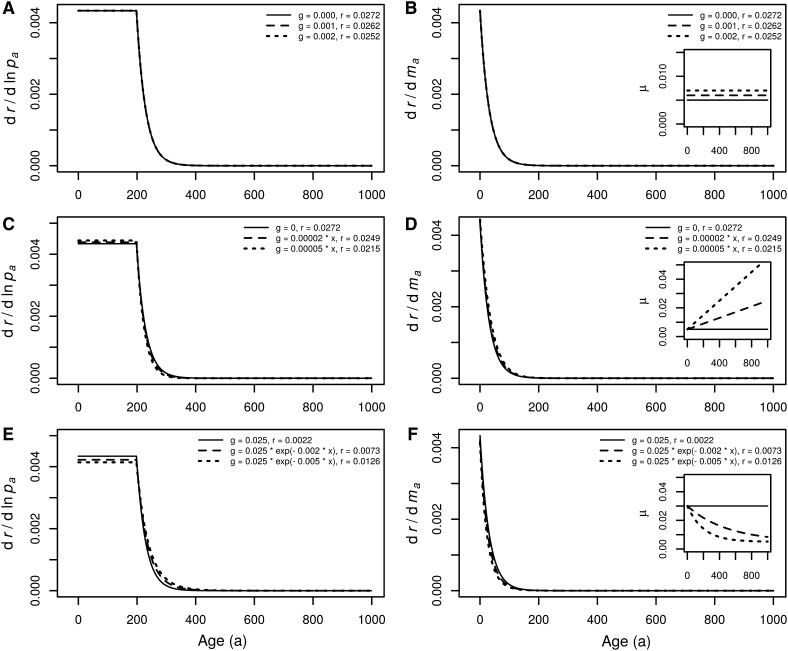
Fig. 1.
Selection gradients for r under different extrinsic mortalities. a, b age-independent extrinsic mortality, c, d extrinsic mortality increasing with age, and e, f extrinsic mortality decreasing with age. Before adding extrinsic mortality, each of the cases has the life-history defined in the same way: the background probability of surviving an age class x (e.g. measured in days) is constant and equal px = 0.995; the fertility mx is 0 before maturity and 20 after maturity; maturity occurs at age 200. Insets show the total age-specific mortality calculated as where g is extrinsic mortality. The Malthusian parameter (r) is calculated from the Euler–Lotka equation, taking into account both background and extrinsic mortality