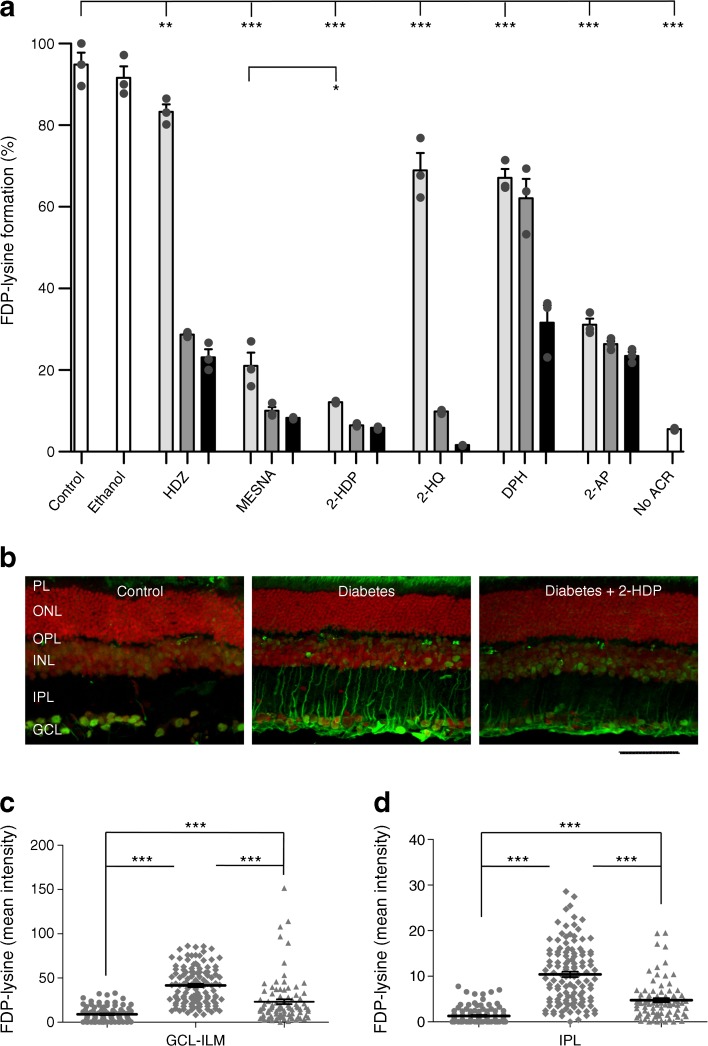
Fig. 1.
(a) FDP-lysine detected using ELISA following conjugation with ACR in the presence of three concentrations of different scavenging molecules (light grey bars, 1.25 mmol/l; medium grey bars, 2.5 mmol/l; black bars, 5 mmol/l), expressed as a percentage of control (no scavenger present; PBS+ACR; data were normalised to the first control replicate). The scavenging molecules tested were: HDZ; MESNA; 2-HDP; 2-HQ; DPH; and 2-AP. Experiments were carried out in triplicate; ethanol (50% ethanol + ACR) and samples with no added ACR (No ACR; PBS only) were included as additional controls. (b) FDP-lysine immunolabelling (green) on retinal cross sections of control, diabetic and 2-HDP-treated diabetic animals; scale bar, 50 μm. Cell nuclei are counterstained with propidium iodide (red). (c, d). Column scatter graphs showing mean pixel intensity from regions of interest randomly selected within the ganglion cell layer-inner limiting membrane (c) and inner plexiform layer (d). Circles, control; diamonds, diabetes; triangles, diabetes +2-HDP; n=6 retinas from six animals in each group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 for the indicated comparisons. GCL, ganglion cell layer; ILM, inner limiting membrane; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; PL photoreceptor layer