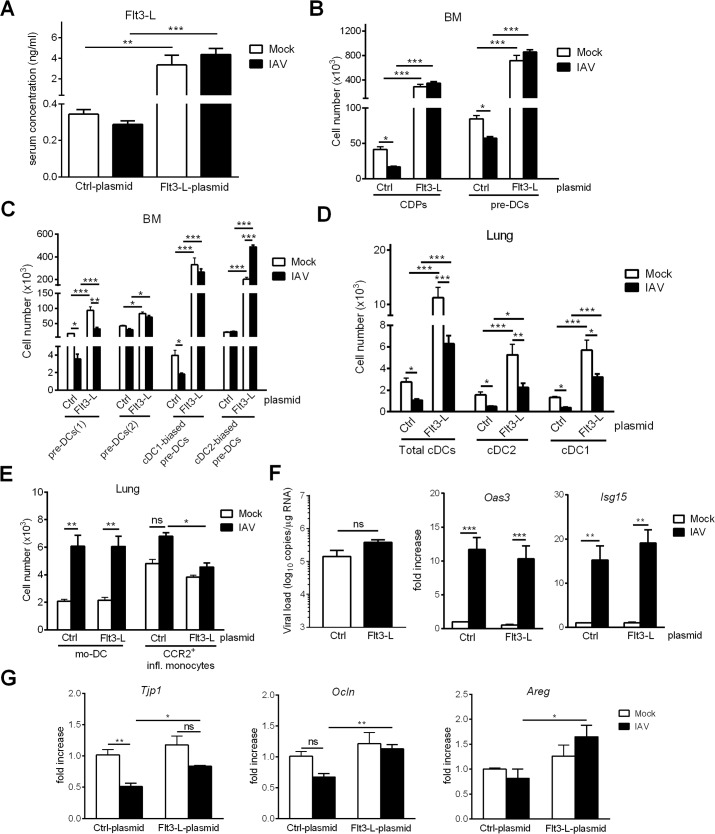
Fig 7. Flt3-L overexpression during IAV infection enhances cDC generation and is associated with an increased expression of genes involved in lung barrier integrity.
Mice were i.v. injected with 2μg of a control- or Flt3-L- encoding plasmid. Twenty four hours later, mice were infected, or not, with IAV. Mice were sacrified at 4 dpi. (A) The production of Flt3-L was quantified in the sera, (B) the numbers of CDPs, total pre-DCs and (C) pre-DC subsets were assessed in the BM by flow cytometry. (D) The numbers of cDC subsets and (E) other myeloid cells were determined in the lungs. (F)(left panel) Viral load (in log10 viral M1 RNA copies/μg RNA) and (middle and right panel) mRNA expression of Oas3 and Isg15 genes were quantified in the lungs (RT-PCR). (G) mRNA copy numbers of genes associated with the barrier integrity (Ocln, Tjp1) and tissue repair (Areg) were determined in the lungs (RT-PCR). All RT-PCR data are normalized to expression of Gapdh and are expressed as fold increase over average gene expression in Ctrl-plasmid/mock animals. Data represent the means ± SEM of biological replicates (A-E) n = 6–12 and (F-G) n = 5. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, ns: not significative.