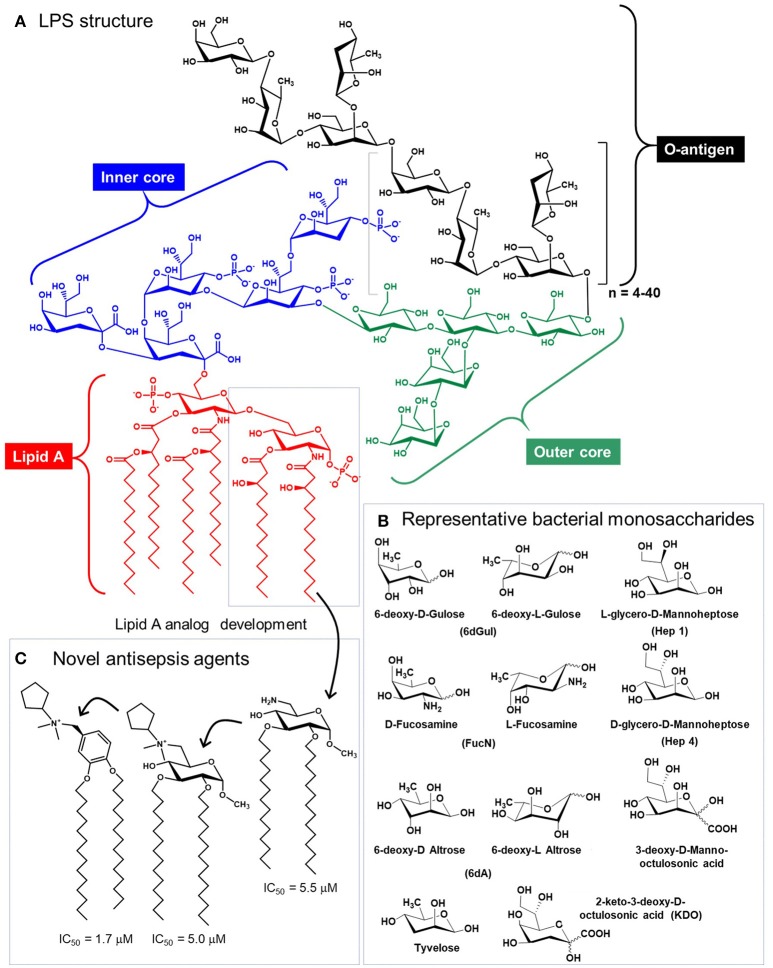
Figure 6.
Structure of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (A) Glycolipids, exemplified by bacterial structures such as LPS contain the Lipid A, and inner core, an outer core, and the O-antigen, which varies based on species and strain [Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhi is show (160)]. (B) LPS glycans contains a variety of non-mammalian monosaccharides, which contributes to their immunogenicity and provokes sepsis [(A,B) are adapted from Saeui et al. (161)]. (C) Medicinal chemistry efforts have exploited the Lipid A structure to create anti-inflammatory analogs [three are shown, from Piazza et al. (162)] that are promising anti-sepsis agents.