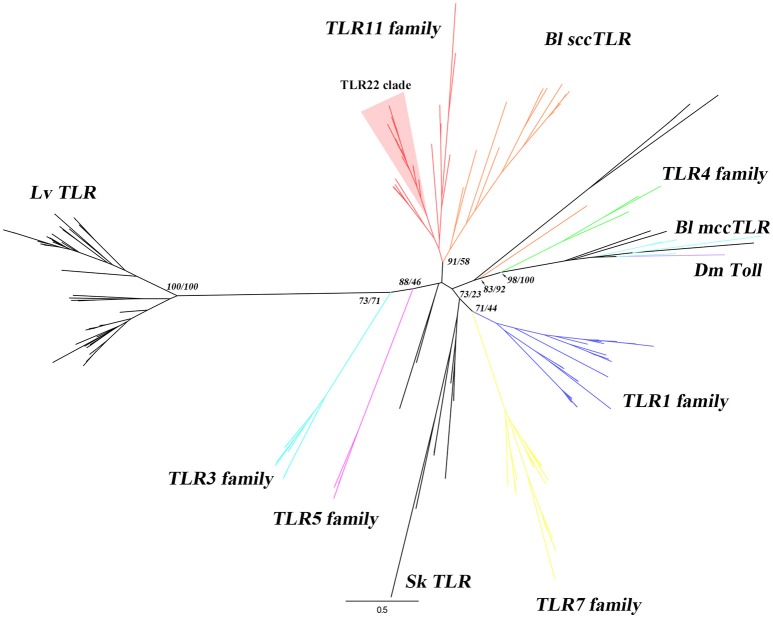
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of B. lanceolatum TLRs. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using maximum-likelihood (IQ-TREE) with the full-length protein sequences. TLR sequences of B. lanceolatum, S. kowalevskii, L. variegatus, representative vertebrates and D. melanogaster Toll were used. Three TLR sequences (Bl10262, Bl22164 and Bl08928c) with incomplete TIR domain were removed from the analysis. Sequences were aligned with MAFFT choosing L-INS-i method and the alignments were trimmed using TrimAL with “Automated 1” mode. The best evolutionary model was established by ModelFinder according to BIC. The branch labels (numbers) are SH-aLRT support (%)/ultrafast bootstrap support (%) at the tree nodes. The tree was generated in FigTree. Dm Toll, Bl mccTLRs, Bl sccTLRs, Sk TLR, Lv TLR and 6 vertebrate TLR families (highlighted in different colors) are shown. TLR22 clade is shown with a red background. The detailed tree with all node supports can be found in Supplementary Figure 2.