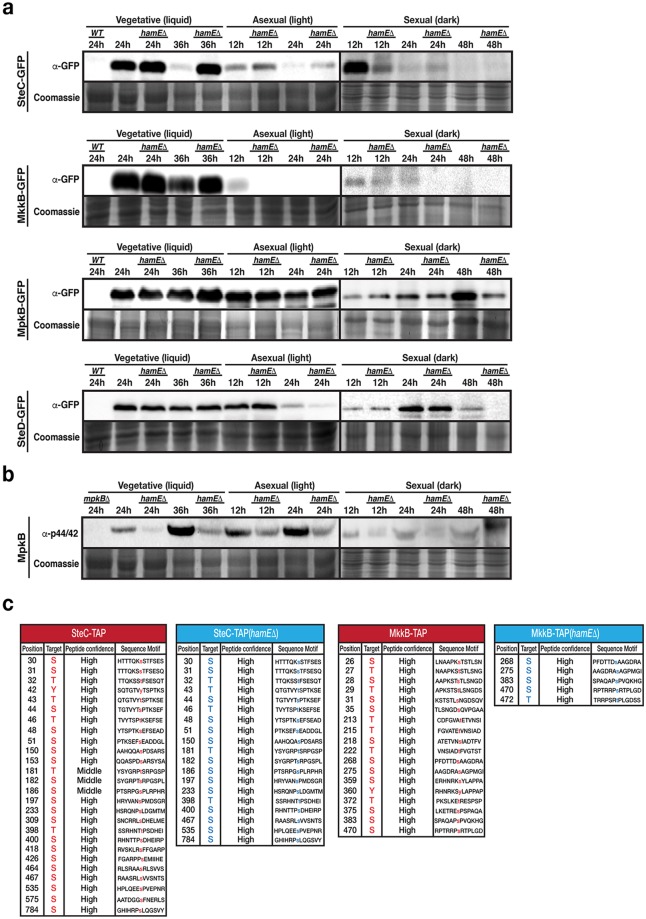
Figure 4.
Expression levels and phosphorylation states of the pheromone module components in the presence and absence of hamE. (a) The expression levels of sGFP-tagged SteC, MkkB, MpkB and SteD fusion proteins were determined at various stages of development in the presence and absence of hamE. Vegetative cultures were grown in liquid GMM media. For asexual and sexual cultures, strains were initially grown for 24 hours vegetatively in liquid GMM media and then mycelia was transferred to GMM plates to be incubated in the light and dark respectively. 80 μg of each protein sample was loaded on 10% acrylamide gels and for loading controls, these gels were stained in 0.1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 dye and exposed using the G: BOX Chemi XRQ (Syngene). Sexual development samples (dark) were run in different gels separated from vegetative and asexual samples by a vertical black line. (b) Determination of the phosphorylation status of MpkB in the presence and absence of hamE using an anti-phospho-p44/42 antibody (Thr182/Tyr184). Sexual samples were run in different blots. SteC samples from part (a) were used for these blots. As a result, coomassie staining controls are the same as those for SteC samples. (c) Comparison of the phosphorylated residues of SteC and MkkB in the presence and absence of hamE. The tables represent the total phosphorylated residues and their amino acid positions detected by mass spectrometry using 4 independent TAP-tagged biological replicates of each strain. S (Serine), T (Threonine), Y (Tyrosine). Full-length blots in (a,b) are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3.