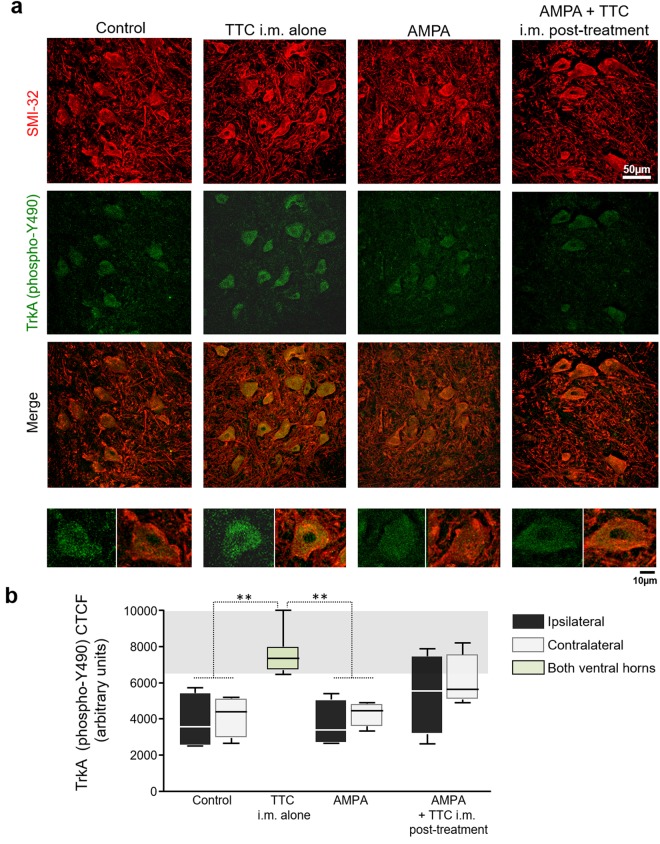
Figure 5.
The i.m. administration of TTC increases TrkA receptor (phospho-Y490) in spinal MNs. (a) Representative confocal micrographs of the ipsilateral ventral horns immunostained for SMI-32 (red) and TrkA (phospho-Y490) (green) in the lumbar section of rats treated as indicated, four days after minipump implantation. The images on the bottom are magnifications of a representative MN with the TrkA (phospho-Y490) labeling (left) and the corresponding merged (right). (b) Quantitative analysis for TrkA (phospho-Y490) in spinal MNs. The TTC i.m. alone group received a bilateral i.m. administration of the fragment, and the green bar represents the average of both ventral horns. The analysis of the corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) was made using the maximum intensity projection of the Z-stack images for TrkA (phospho-Y490) alone. CTCF shows that TTC i.m. alone increased the phosphorylation of the TrkA receptor at Y490 in spinal MNs. Five histological slices/rat were analyzed (n = 4 per group). The boxes represent the 1st and 3rd quartile around the median. The whiskers above and below the box show the locations of the minimum and maximum values. The grey horizontal area highlights the maximum and minimum value for the AMPA group. **p < 0.01 vs the AMPA group.