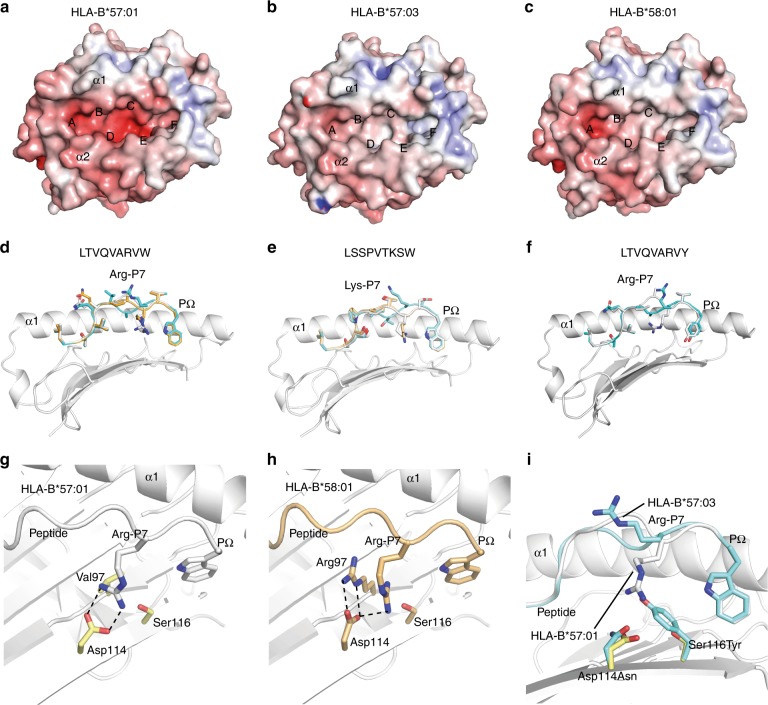
Fig. 4.
HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*57:03 and HLA-B*58:01 present peptides in distinct conformations. a–c The electrostatic potential mapped to the surface of the structures of HLA-B*57:01, HLA-B*57:03 and HLA-B*58:01 respectively (red—electronegative, blue—electropositive). The α1 and α2 helices and the positions of peptide-binding pockets A–F are shown. d–f Superposition of the crystal structures of the LTVQVARVW, LSSPVTKSW and LTVQVARVY peptides (respectively) in complex with HLA-B*57:01 (grey), B*57:03 (cyan) and B*58:01 (orange). The α2 helix has been removed for clarity. g The interaction between the P7Arg (from the peptide LTVQVARVW) and Asp114 in HLA-B*57:01. h The interaction between the P7Arg (from the peptide LTVQVARVW) and Asp114 in HLA-B*58:01. i Superposition of the LTVQVARVW peptides in complex with HLA-B*57:01 (grey) and B*57:03 (cyan). The presence of the Ser116Tyr micropolymorphism (HLA-B*57:01–>HLA-B*57:03) prevents the binding of the P7Arg in the E pocket of HLA-B*57:03