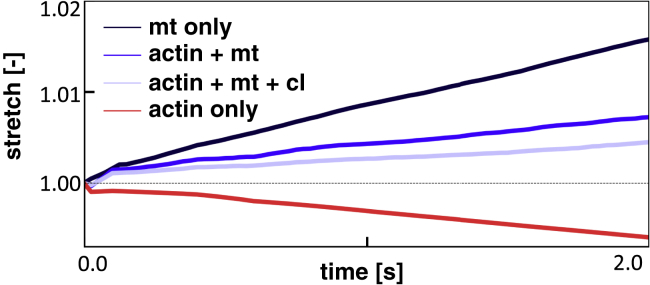
Figure 5.
Axon stretch versus time for different configurations of the computational model. Located in the key, “mt only” consists only of microtubules with dynein proteins and, similarly, “actin only” includes only actin filaments with myosin proteins. These two systems are combined in actin + mt. Finally, the two systems are connected by dynein cross-links between actin filaments and microtubules in actin + mt + cl. The applied external load, , is equal for all for simulations. The results demonstrate the competition between extensile dynein forces and contractile myosin forces. The addition of cross-links between microtubules and actin leads to an increase in passive viscosity of the axon that reduces the axon stretch. To view this figure in color, go online.