Figure 2.
Correction of the Pathogenic FBN1T7498C Mutation by Base Editing in Human Cells
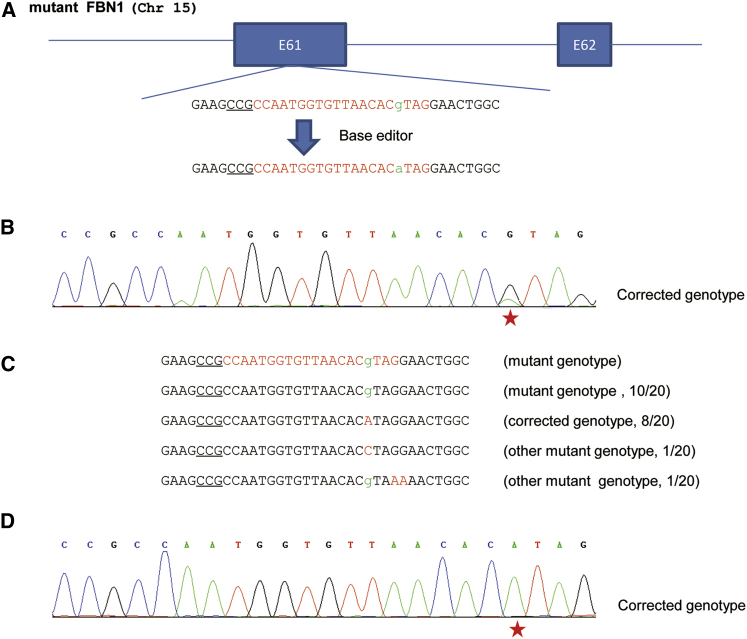
(A) Schematic illustration of the correction of the pathogenic FBN1T7498C mutation. The “g” in lowercase highlighted in green at the targeted site was substituted by a “g” in lowercase in green. The PAM sequences are underlined; the targeting sequence is highlighted in red. (B) The representative chromatogram of the sequencing of PCR products. The cells harboring the FBN1T7498C mutation were transfected with sgRNA and BE3-expressing plasmids. The cells were collected, and the genomic DNA was extracted and amplified by PCR. The PCR products were analyzed by DNA sequencing. The red star indicates the substituted base. (C) Sequencing analysis of the base editing. TA clones of the PCR products from (B) were analyzed by DNA sequencing. The PAM sequences are underlined; the targeted bases in lowercase are highlighted in green; the modified bases in red; the N/N represents positive colonies out of the total sequenced. (D) The representative chromatogram of the sequencing of TA clones. TA clones from (C) were sequenced. The red star indicates the substituted base.