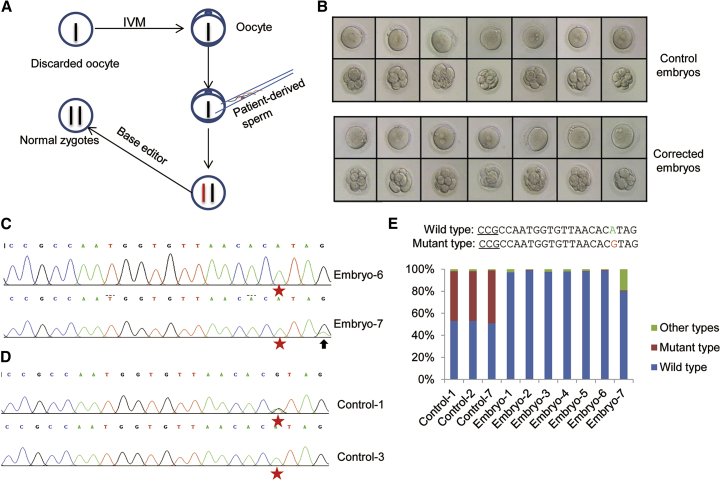
Figure 3.
Correction of the Pathogenic FBN1T7498C Mutation by Base Editing in Heterozygous Human Embryos
(A) Schematic illustration of the experimental procedure for the correction of the pathogenic mutation by base editor in human embryos. (B) The development stage of the corrected embryos and the control embryos before and after treatment. (C) The representative chromatogram of the sequencing of PCR products from the corrected human embryos. The human embryos treated with base editor were collected, and the genomic DNA was extracted and amplified by PCR. The PCR products were analyzed by DNA sequencing. The red stars indicate the target base; the arrow indicates another base substitution in the target region. (D) The representative chromatogram of the sequencing of PCR products from the control human embryos. The control human embryos were collected, and the genomic DNA was extracted and amplified by PCR. The PCR products were analyzed by DNA sequencing. The red stars indicate the target base; the mixed peaks at the target site in Control-1 indicate the different kinds of nucleotides. (E) The genotyping analysis by deep sequencing. All of the samples, including three control and seven corrected human embryos, were collected, and the genomic DNA was extracted and amplified by PCR. The PCR products were analyzed by deep sequencing. The percentage of different genotypes of all samples was calculated.