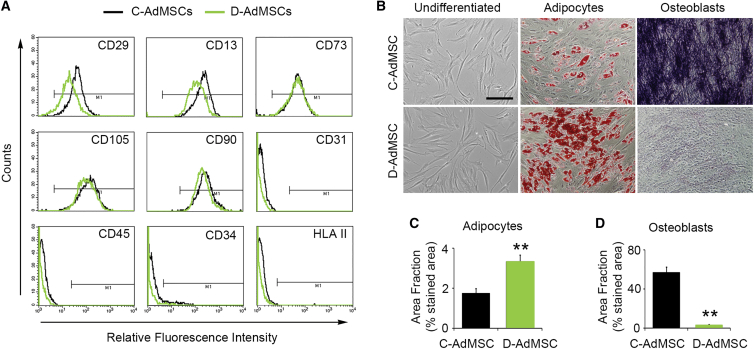
Figure 1.
Characterization of C-AdMSCs and D-AdMSCs
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of cultured AdMSCs showing that both control and diabetic cells were positive for the MSC-specific markers CD29, CD13, CD73, CD105, and CD90, whereas they were negative for CD31, CD45, CD34, and HLA II. Respective isotype controls were used to define gate M1 and discard non-specific staining (less than 1%). (B) Phase contrast image of primary subconfluent cultures of C-AdMSCs and D-AdMSCs showing typical adherent fibroblast-like morphology, adipogenic differentiation (demonstrated by the presence of lipid droplets stained with oil red O), and osteogenic differentiation (demonstrated by alkaline phosphatase activity). (C) Quantification of the area occupied by the oil red O staining. (D) Quantification of the area occupied by the alkaline phosphatase staining. Scale bar: 100 μm in (B). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 (two-tailed t test).