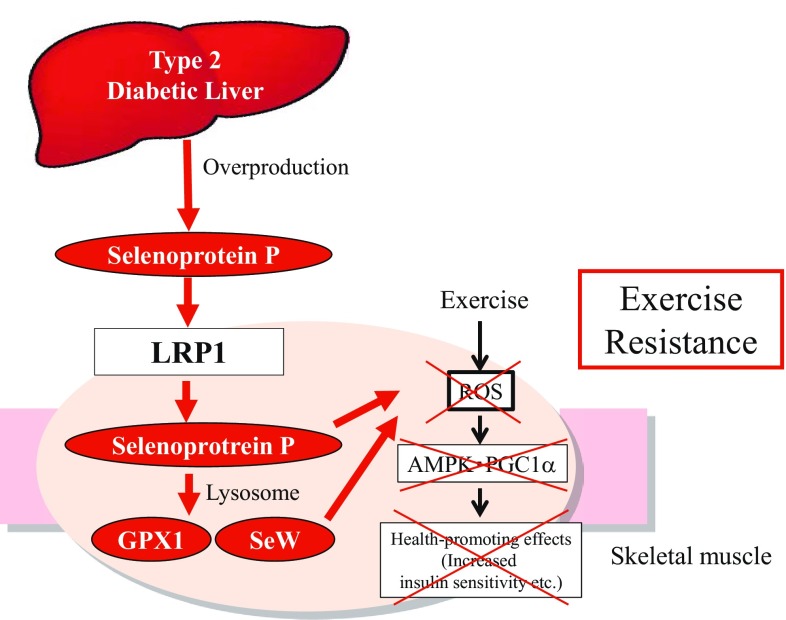
Fig. 5.
Overproduction of selenoprotein P impairs the health-promoting effects of exercise by inhibiting ROS (reactive oxygen species)/AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase)/PGC-1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α) pathway in the skeletal muscle through its receptor LRP1 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1). Selenoprotein P suppresses ROS generation by directly acting as an anti-oxidative enzyme and indirectly inducing the other selenoproteins such as glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) and selenoprotein W (SeW)