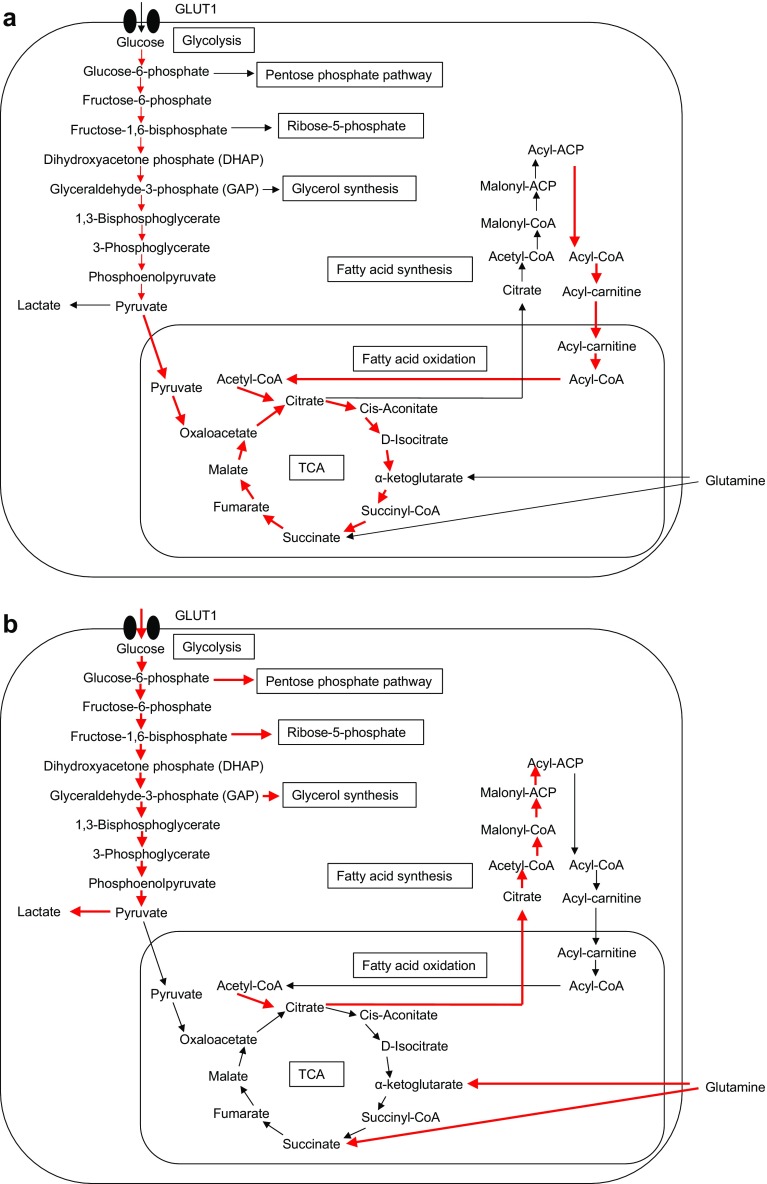
Fig. 1.
Metabolic pathways of aerobic glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). a Normal resting cells, such as M2 macrophages, conventional dendritic cells (DCs) and naïve and memory T cells, generate ATP through a combination of glycolysis and mitochondrial OXPHOS by the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. b Actively proliferating cells, such as cancer cells, activated DCs, activated M1 macrophages, and effector T cells, switch metabolism from OXPHOS to aerobic glycolysis. GLUT1 Glucose transporter-1, ACP acyl-carrier protein, CoA coenzyme A