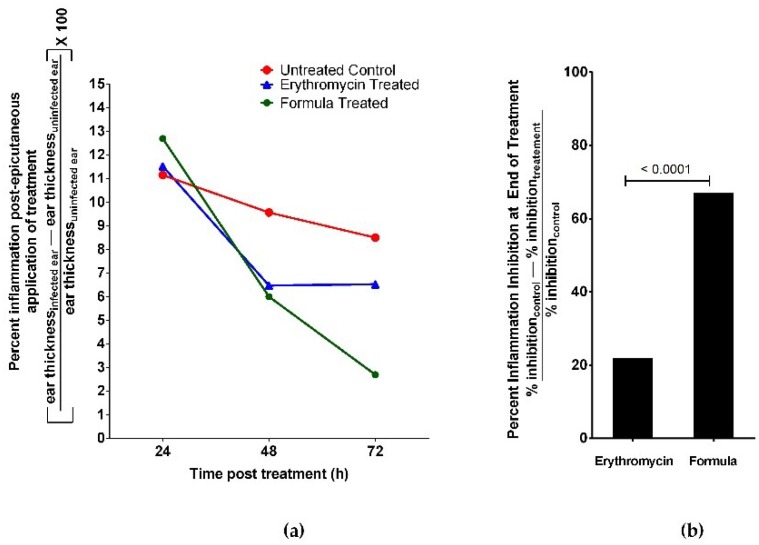
Figure 4.
Oregano EO nanoemulsion showed stronger inhibition of inflammation than erythromycin control in acne mouse model. The acne mouse model was induced by intradermal injection of BALB/c mice’s left ears with 108 CFU in 20 mL of P. acnes. The mice’s right ears served as uninfected control. We applied epicutanously either oregano EO nanoemulsion or 2% Erythromycin solution on the infected mice ears. A third group of mice served as untreated control. (a) Percent inflammation was assessed post epicutaneous application of treatment as the difference between each mouse ear thickness of infected and uninfected ears. Oregano nanoemulsion showed higher rate of reduction in inflammation than 2% erythromycin during the treatment time interval. (b) Oregano nanoemulsion showed significantly higher percent of inhibition of inflammation (>60%) at the end of treatment period than 2% erythromycin control (20%). Data represented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments, total mice per group 15 mice. We used t-test for comparing groups with p < 0.05 consider significant.