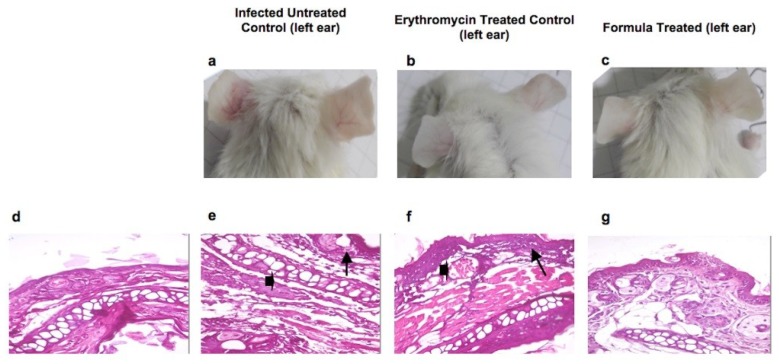
Figure 5.
Oregano nanoemulsion as a potent anti-acne agent tested in vivo model of P. acnes infection Photo images of BALB/c mice ear skin at the end of the experiment showing (a) untreated control mice, one ear injected with 20 μL of 108 CFU P. acnes suspension showing microcomedones and inflammation in infected left ear compared to the uninfected right ear; (b) inflammation in left infected ear disappeared after treatment with erythromycin solution comparable to the right uninfected ear; (c) absence of inflammatory appearance in left infected ear treated by oregano formula; (d) histopathological analysis of uninfected mice ear skin tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin showing normal histology of mouse ear tissue with basal layer and epidermal cell maturation preserved; (e) histopathology of infected untreated control mice ear showing necrotic dermatitis character; note the severe dermal necrosis (arrow head), and lymphocytic infiltrate (arrow); (f) ear showing acute dermatitis character; note the congested blood vessels (arrow head), and slight lymphocytic cells infiltration (arrow) treated by erythromycin solution; (g) ear showing apparently normal histology of mouse ear tissue with the absence of inflammatory reaction, treated with oregano formula.