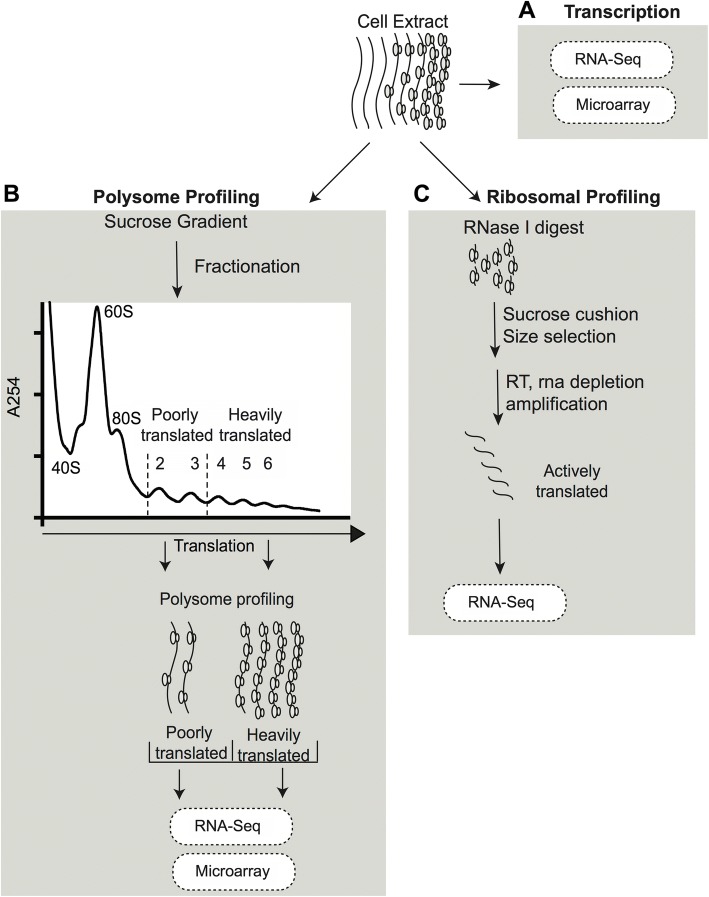
Fig. 1.
Genome-wide translatome assays. a. Schematic of polysome profiling and ribosome profiling. Cytoplasmic mRNA is first isolated and subjected to density ultracentrifugation in both methods where mRNAs bound to ribosomes are separated based on weight and velocity. A sample of cytoplasmic mRNA is maintained for downstream analysis. b. In polysome profiling, ribosome-bound mRNAs are further fractionated based on ribosomal RNA content and segregated into fractions based on bound number of ribosomes. Collected fractions of ribosome-bound mRNAs can be pooled based on ribosome number to analyze different levels of translation. The cytoplasmic sample and polysome sample or samples are then subjected to microarray analysis or RNA sequencing. c. In ribosome profiling, ribosome-bound mRNAs are subjected to RNase treatment prior to ultracentrifugation, which digests naked mRNA leaving 23–27 nt fragments of ribosome-protected mRNA. These fragments are size-selected and amplified. The cytoplasmic sample and footprint sample are then subjected to RNA sequencing