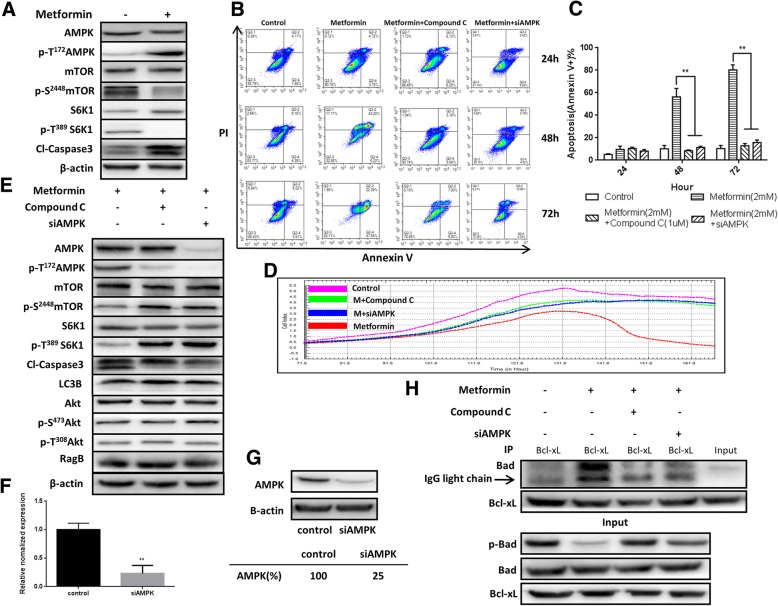
Fig. 3.
Metformin induces the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated apoptosis. a AMPK, mTOR, S6K1, their phosphorylated forms, and cleaved-caspase 3 were assessed by western blot analysis after treatment with or without metformin (2 mM). β-actin was used as loading control. b, c Treatment with an AMPK inhibitor (compound C) (1 μM) and siAMPK significantly blocked metformin-induced hUC-MSC apoptosis. Bars in c represent the mean ± SD (n = 3 per group). **p < 0.01, by one-way ANOVA. d Real-time cellular analysis (RTCA) of compound C and siAMPK on metformin-induced hUC-MSC apoptosis. e Compound C and siAMPK significantly inhibited metformin-induced AMPK phosphorylation but have no effect on LC3B, Akt, and Rag B. β-actin was used as loading control. f, g Expression of AMPK in hUC-MSCs 24 h after transient transfection of siAMPK at the transcriptional (qRT-PCR, **p < 0.01, by t test, n = 3) and translational (western blot) level. h hUC-MSCs were treated with metformin (2 mM) with or without compound C (1 μM) and siAMPK for 36 h. After treatment, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Bcl-xL antibody and immunoblotted with an anti-Bad antibody. The presence of Bad and Bcl-xL in the lysates was examined. The results are representative of three independent experiments