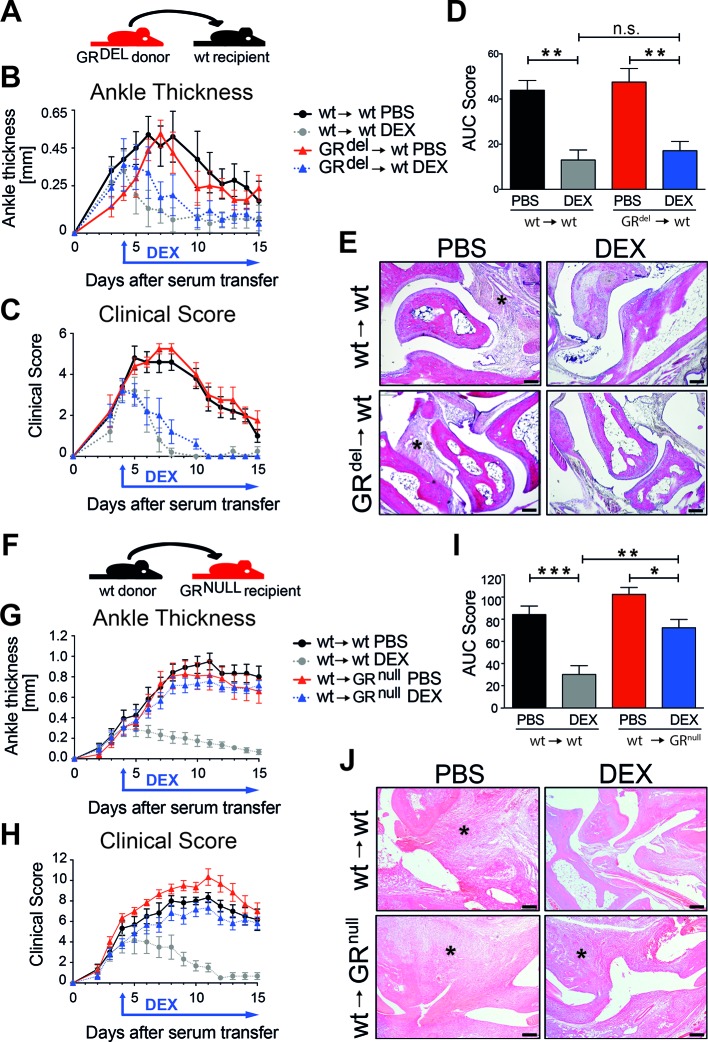
Figure 1.
GR deficiency in stromal cells abrogates anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoid (GC) treatment in serum transfer-induced arthritis (STIA). (A) Scheme of fetal liver cell transfer into irradiated wt recipient mice. Mice were either reconstituted with wt donor fetal liver cells (wt→wt) or with GR-deficient donor fetal liver cells (GRdel→wt). (B) Ankle thickness and (C) clinical score of mice treated with PBS (black and red) or DEX (grey and blue). (D) AUC of the clinical score of mice treated with PBS (black and red) or DEX (grey and blue). (E) H&E staining of paraffin sections of hind paws of wt→wt and GRdel→wt mice (scale bar=200 µm); asterisks show the area of inflammation. Group size n=5 mice per group. (F) Scheme of bone marrow transplantation of irradiated wt and GR-deficient recipients with wt donor bone marrow cells (wt→wt and wt→GRnull). (G) Ankle thickness and (H) clinical score of mice treated with PBS (black and red) or DEX (grey and blue). (I) AUC of the clinical score of mice treated with PBS (black and red) or DEX (grey and blue). (J) H&E staining of paraffin sections of hind paws of wt→wt and wt→GRnull mice (scale bar=200 µm); asterisks show area of inflammation. Group size n=5 mice per group. AUC, area under the curve; DEX, dexamethasone; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; ns, not significant; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; wt, wild type.