Figure 5. The canonical initiation factor eIF1/SUI1 may not play a role in recycling of post-termination 40S ribosomes.
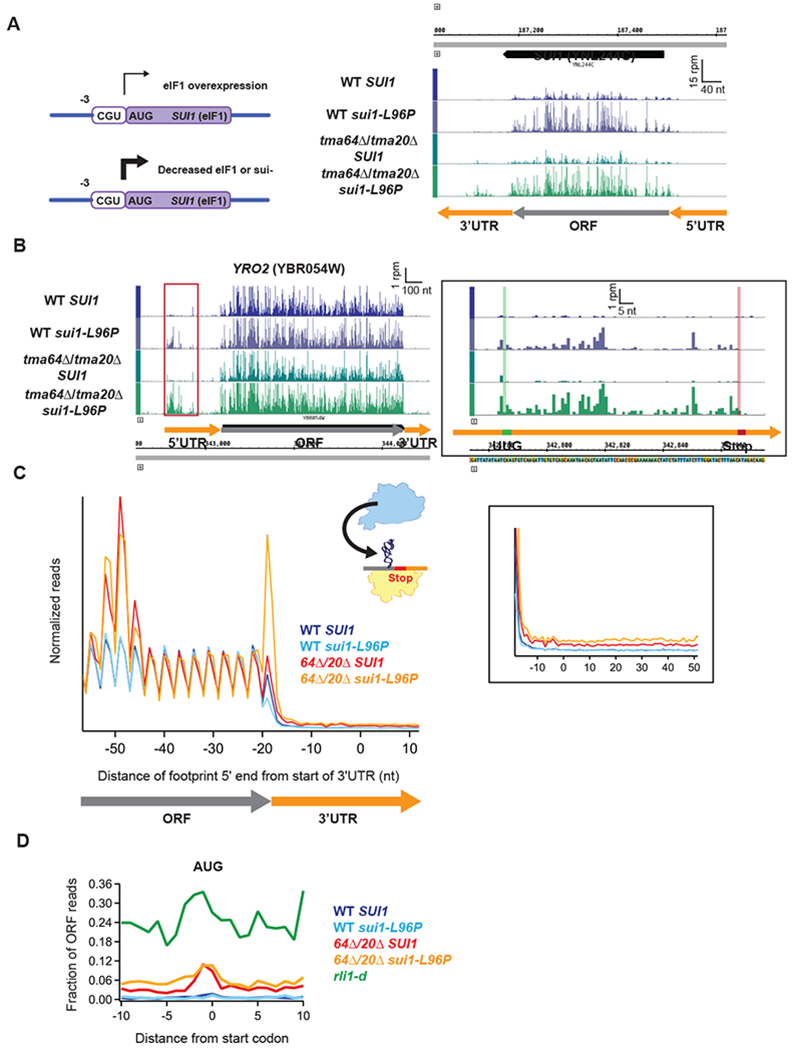
(A) Diagram showing the translational autoregulation of the SUI1 gene (left). The eIF1 AUG start codon is in poor context (C at the −3 position), making it sensitive to changes in the expression level of eIF1. (Right) Genome view of the SUI1 gene showing increased ribosome occupancy in the strains carrying the sui1-L96P allele, confirming the expected Sui− phenotype. Gene annotations correspond to ribosome P sites (AUG codons) or A sites (stop codons).
(B) Genome view of YRO2 showing increased ribosome occupancy in the 5’UTRs of the strains carrying the sui1-L96P allele. (Inset) Close-up of red box showing a UUG-initiated uORF. Reads are shifted so peaks approximately correspond to ribosome P sites.
(C) Normalized average ribosome footprint occupancy (each gene weighted equally) from all genes aligned at their stop codons for WT SUI1, WT sui1-L96P, tma64Δ/tma20Δ SUI1, and tma64Δ/tma20Δ sui1-L96P cells. The schematic depicts reassociation of a 60S subunit to a 40S subunit stalled at the stop codon. Footprint 5’ ends are plotted. (Inset) Zoomed-in view of the 3’UTR.
(D) Average fraction of ribosome occupancy in a window surrounding 3’UTR AUG codons normalized to ORF ribosome occupancy level (all frames included). Reads are shifted so peaks approximately correspond to P sites.
