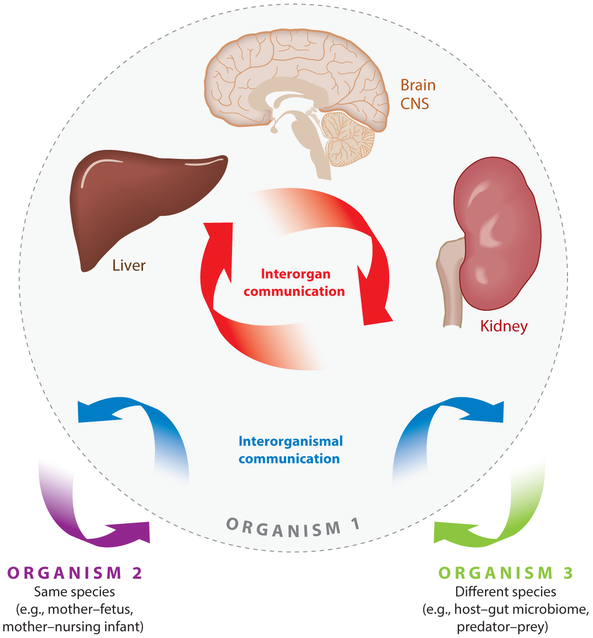
Figure 3.
The role of SLC22 transporters in remote sensing and signaling. The remote sensing and signaling hypothesis argues that SLC22 transporters and other SLC and ABC drug and nondrug transporters are part of a large interorgan and interorganism small-molecule communication network that maintains homeostasis in epithelial and nonepithelial tissues and body fluid compartments, such as blood, bile, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. This remote sensing and signaling system in SLC and ABC transporters is hypothesized to work in parallel with the neuroendocrine and growth factor–cytokine systems and is, indeed, intertwined with them. Figure adapted from Reference 1. Abbreviation: CNS, central nervous system.