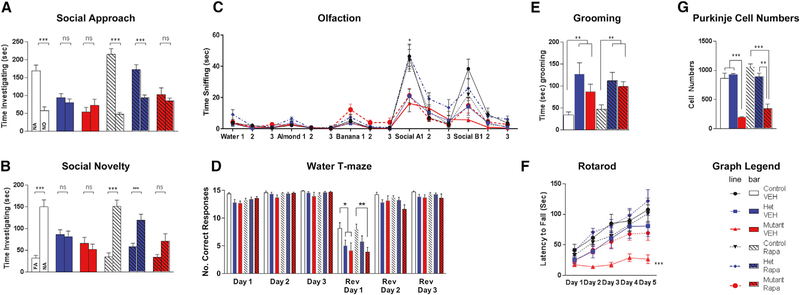
Figure 4. At 10 Weeks, Sensitive Period Is Open for Social Behaviors in the Presence of PC Survival.
(A–C) Rapamycin initiated at 10 weeks is able to rescue social behaviors in (A) social approach, (B) social novelty, and (C) social olfaction behavioral paradigms only in heterozygous (het), not homozygous (mutant), PC Tsc1 mutants.
(D and E) No rescue is seen for either genotype in (D) reversal learning in water T maze or (E) with repetitive grooming.
(F) Despite these findings, persistent rescue of motor learning on the rotarod was observed in homozygous PC Tsc1-mutant mice.
(G) PC viability is not rescued in homozygous PC Tsc1 mutants with rapamycin initiated at 10 weeks of age.
Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. FA: familiar animal; NA, novel animal; NO, novel object; Ns, not significant; Rapa, rapamycin; Rev, reversal; VEH, vehicle. Data are reported as mean ± SEM.