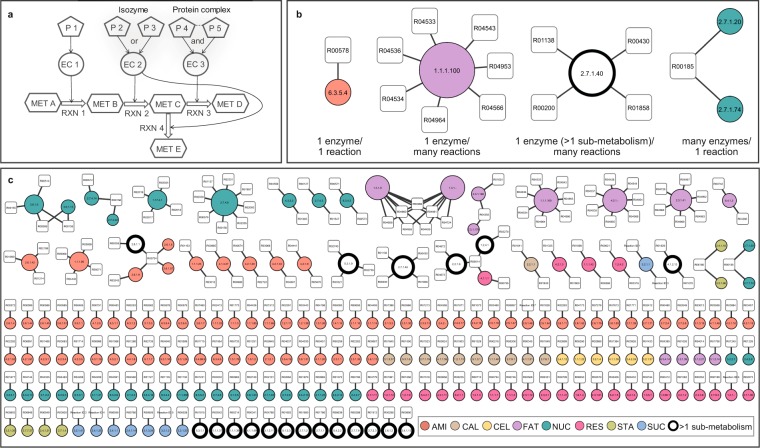
Figure 4.
The complexity of the carbon assimilation metabolic pathway of cassava based on reaction-enzyme association. (a) The schematic of relationship among annotated enzymatic proteins (P), enzymes (EC), enzymatic reactions (RXN), and metabolites (MET); (b) Examples of the reaction-enzyme association in MeRecon; (c) The relationship between enzymes (EC numbers) and reactions in MeRecon, represented as nodes and edges. Nodes consist of enzymes (circles) and enzymatic reactions (rectangles), and the edges between the nodes represent reaction-enzyme association of each metabolic reaction. Size of enzyme nodes represents node degree, and the number of enzymatic reactions catalyzed by that enzyme. AMI - amino acid biosynthesis, CAL - Calvin cycle, CEL - cell wall biosynthesis, FAT - fatty acid biosynthesis, NUC - nucleotide biosynthesis, RES – respiration, STA - starch biosynthesis, and SUC - sucrose biosynthesis.