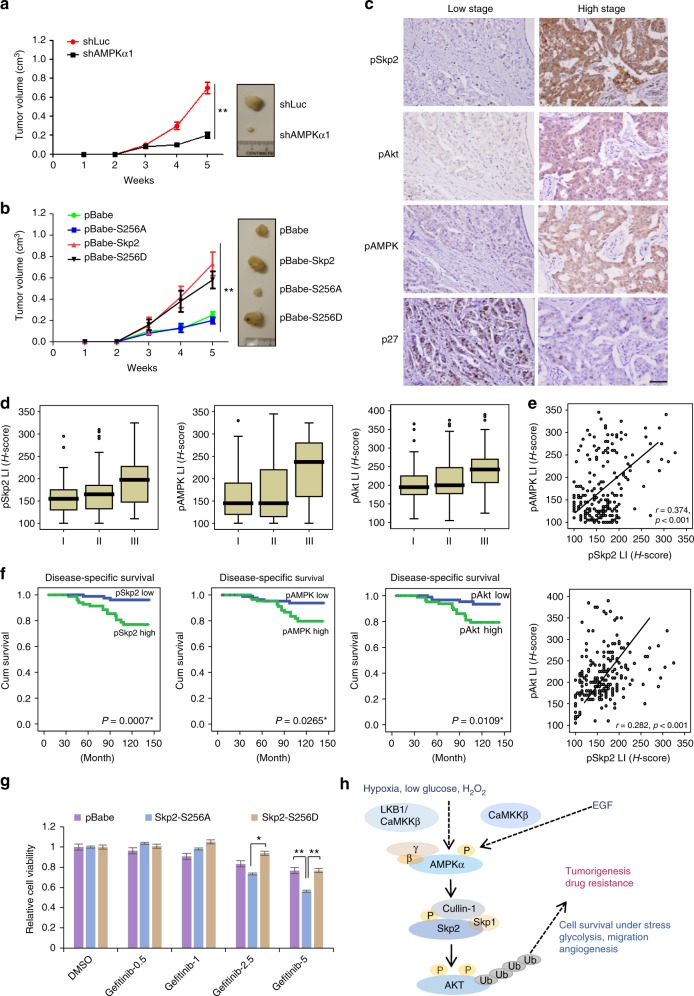
Fig. 6.
AMPK-mediated Skp2 S256 phosphorylation and Akt activation promotes cancer progression, predicts poor survival outcome and contributes to resistance of EGFR targeting therapy. a MDA-MB-231 cells with control (shLuc) and AMPKα1 knockdown were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. Tumor size was measured by the caliper, and the result was showed as means ± SEM. (n = 5). **P < 0.01. b MDA-MB-231 cells with stable expression of the indicated pBabe-Skp2 WT, S256A and S256D were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. Tumor size was measured by the caliper, and the result is shown as means + SEM (n = 5). **P < 0.01. c pSkp2 (S256) and pAMPK are upregulated in breast cancer patients. Representative images of histological analysis of pSkp2 (S256), pAkt, pAMPK and p27 staining in early (Left panel) and late-stage human breast cancer (Right panel). Scale bar, 200 μm. d Overexpression of pSkp2 (S256) and pAMPK are detected in advanced stage of breast cancer patient. Box plot represents pSkp2 (S256), pAMPK and pAkt expression in different stages of breast cancer patient. **P < 0.01. e pAMPK and pAkt expression both correlate with pSkp2 (S256) in breast cancer patients. Scatter plots of pSkp2 (S256) expression vs. pAMPK (Upper panel) and pAkt (Lower panel) expression in breast cancer patient were presented. f Overexpression of pAMPK, pSkp2 and pAkt predicts poor survival outcome of breast cancer patients. Kaplan–Meier plots showed that high expression of pAMPK (Left panel), pSkp2 (S256) (Middle panel) and pAkt (Right panel) significantly predicted disease-specific survival. p-values are shown in the graphs. g Gefitinib-resistant H1975 NSCLC cells with stable expression of the indicated vector, pBabe-Skp2 S256A and S256D were treated with Gefitinib at indicated concentrations for 72 h, and cell viability was measured by Cell counting kit 8. Columns, mean (n = 3); bars, mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. h Hypothetic model of the role of AMPK in diverse stresses and EGF-induced Akt activation and tumorigenesis