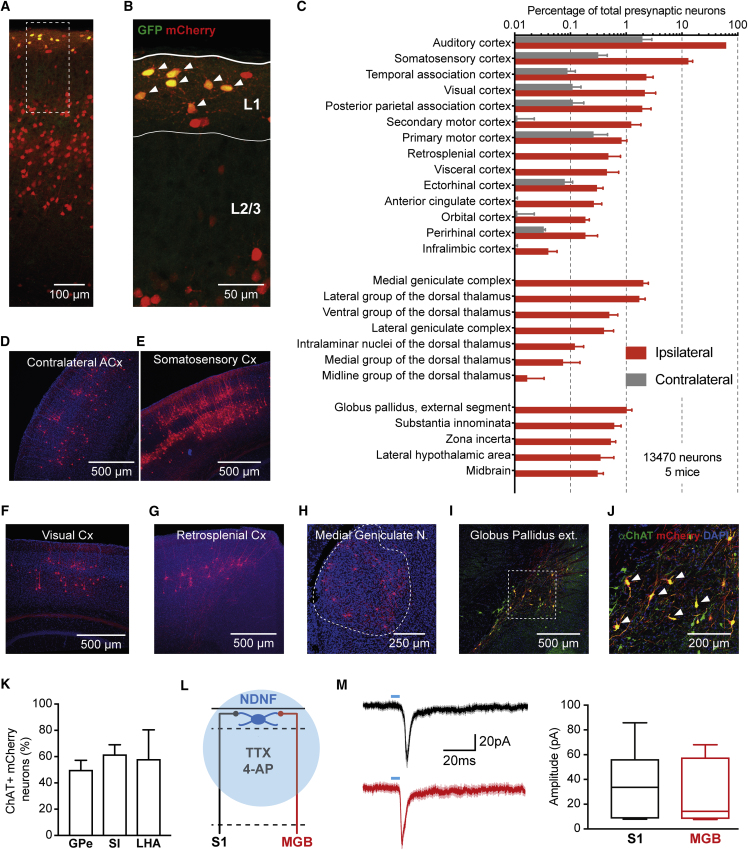
Figure 4.
Brain-wide Sources of Synaptic Input to Auditory Cortex Layer 1 NDNF-Interneurons
(A) Representative image of the injection site in the adult auditory cortex. L1 NDNF-INs were made competent for rabies virus by injection of AAV-synP-DIO-sTpEpB (Kohara et al., 2014) and subsequent tamoxifen induction in Ndnf-Ires-CreERT2 mice. After 4–5 weeks of expression time, RV-dG-mCherry was injected at the same site. Note localization of starter cells expressing both GFP and mCherry in L1 and presynaptic partners in both L1 and deeper layers.
(B) Magnified view of the area indicated in (A). Starter L1 NDNF-INs are marked by arrowheads.
(C) Brain-wide input map to auditory cortex L1 NDNF-INs obtained by referencing mCherry cells (13,470 neurons from 5 animals) to the Allen Brain Atlas (Fürth et al., 2018). This analysis reveals a large number of cortical (top), thalamic (center), and other areas (bottom) that provide afferent input to auditory cortex L1 NDNF-INs.
(D–H) Representative images of the indicated areas.
(I and J) Image of mCherry-expressing neurons in globus pallidus externus counterstained for ChAT, identifying several input neurons in this area to be cholinergic (I); arrowheads in (J), high magnification.
(K) Approximately half of the mCherry-expressing neurons in the globus pallidus externus (GPe), substantia innominate (SI), and lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) were ChAT positive, revealing substantial cholinergic input to auditory cortex L1 NDNF-INs from these areas.
(L) Anterograde physiological validation of the strongest cortical (somatosensory cortex [S1]) and strongest thalamic (medial geniculate body [MGB]) input sources.
(M) Optogenetic stimulation of these axons under action potential block by TTX and 4-AP to prevent polysynaptic input elicits excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSCs) of comparable amplitude in auditory cortex L1 NDNF-INs (n = 7 each, p > 0.05, unpaired t test), confirming that rabies virus tracing identifies true synaptic connectivity.
Data in (M) represent range, quartiles, and median; other plots show mean ± SEM.