Figure 7.
PD2a1 and PD2b1 Mediate Innate Olfactory Attraction, Leading to a Model of Aversive Memory Retrieval
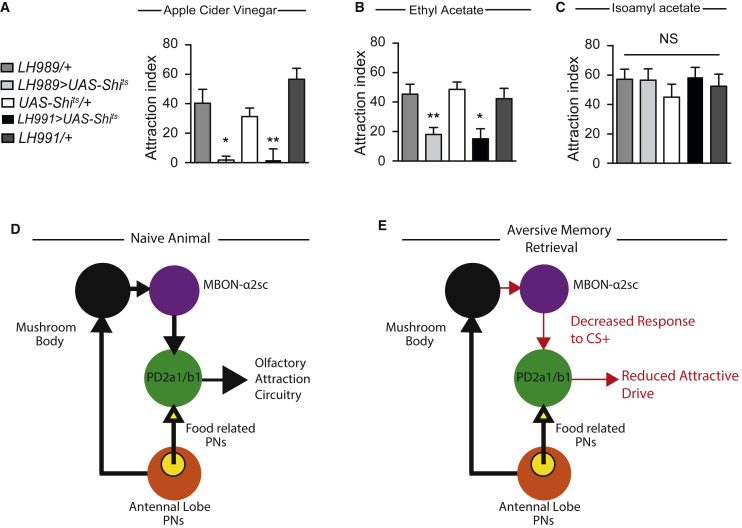
(A) Flies expressing Shits driven by either LH989 or LH991 showed impaired attraction to apple cider vinegar relative to their genotype controls at the restrictive temperature (n = 9, F(4,44) = 12.10, p < 0.0001).
(B) Flies expressing Shits driven by either LH989 or LH991 showed impaired attraction to ethyl acetate relative to their genotype controls at the restrictive temperature (n = 13-16, F(4,73) = 6.34, p = 0.0002).
(C) Flies expressing Shits driven by either LH989 or LH991 showed impaired attraction to isoamyl acetate relative to their genotype controls at the restrictive temperature (n = 8-9, F(4,42) = 0.53, p = 0.72).
(D and E) Model for how PD2a1 and PD2b1 functions in naive and trained animals.
(D) In naive animals, PD2a1 and PD2b1 receives input from both the MB (black sphere, via broadly tuned MBON-ɑ2sc) and directly from the AL food-related PNs (yellow sphere within AL). PD2a1 and PD2b1 activity is necessary for approach behavior to some olfactory stimuli.
(E) After conditioning, the response of MBON-ɑ2sc to the CS+ is reduced via synaptic depression at the MB-to-MBON synapse. This results in a decreased response to the CS+ in PD2a1 and PD2b1. Because PD2a1 and PD2b1 are cholinergic and excitatory, this reduces the input onto downstream approach circuits, resulting in decreased attraction to the CS+ during memory recall.
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. See also Figure S10.