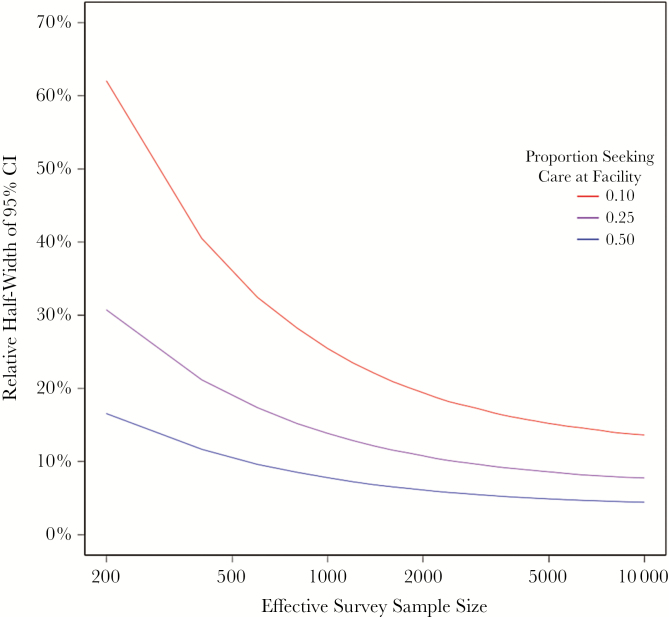
Figure 2.
Relative half-width of the 95% confidence interval (CI) achieved by hybrid surveillance as a function of effect sample size (ie, number of households with an individual meeting study definition for febrile illness) and fraction of patients captured at study sites. Here, incidence is 500 per 100000 and the population size is 500000. A higher proportion of participants seeking care at the facility improves the precision of the adjustment factor estimate as well as the precision in the numerator, as more typhoid cases present to the facility. A larger healthcare utilization sample size can improve precision in the adjustment factor estimate, but greater uncertainty in the incidence estimate remains due to uncertainty in the case number.