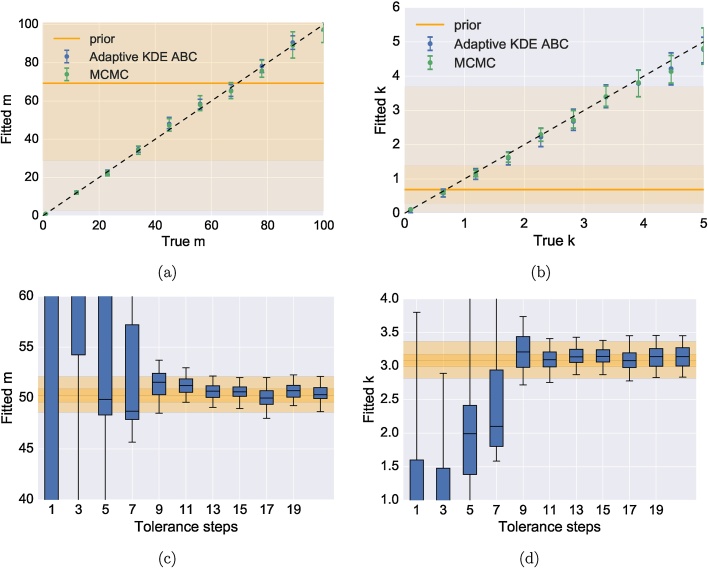
Fig. 2.
Comparison between MCMC and ABC methods for fitting a negative binomial distribution for a range of mean, m and heterogeneity k. (a) Comparison between fits for different mean values m, the dashed line represents the true values and the shading represents the 95% and percentile range of the prior distribution, with the median given as a solid line. The prior distribution was kept fixed for each fitting. The adaptive KDE scheme closely matches the MCMC scheme for all values considered. When the resulting fit is biased for ABC, it is also biased in the same way for MCMC providing confidence that the scheme is approximating the true posterior. (b) Comparison between MCMC and the adaptive ABC scheme for heterogeneity k. As both the MCMC scheme and adaptive ABC scheme underestimate the true value in a consistent way due to the influence of the prior. Comparison between fitted distributions of the adaptive ABC scheme against the number of adaptive tolerance steps are shown for (c) m and (d) k. The true posterior calculated using MCMC is represented as a series of shaded regions with the 95% credible interval, 50% credible interval, and the median shown from lightest to darkest respectively. (For interpretation of the references to color in text/this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)