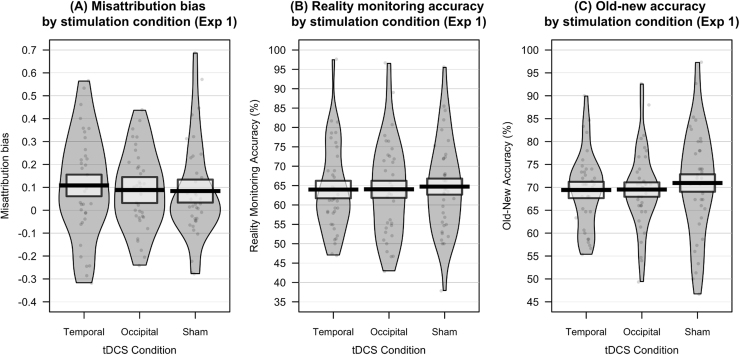
Fig. 1.
A: Misattribution bias: higher values correspond to a higher likelihood of external misattributions when errors are made. B: Reality monitoring accuracy: the percentage of trials on which participants made correct source judgements, for items correctly recalled as old. C: Old–new accuracy: the percentage of trials on which participants correctly classified items as old or new. Solid line = mean performance. Box = 95% confidence interval. Violin = smoothed density. Violin plots were generated in R, using the ‘yarrr’ package.