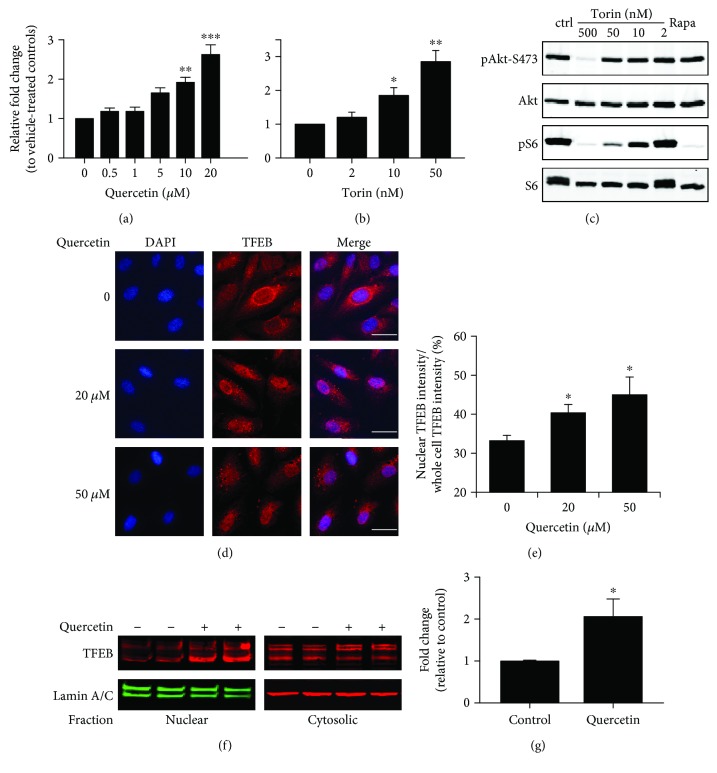
Figure 1.
Activation of TFEB by quercetin in cultured ARPE-19 cells. (a, b) Transcriptional activity of TFEB as measured by the luciferase reporter assay. ARPE-19 cells were transfected with the CLEAR-Luc plasmid and measured for dose-dependent responses to quercetin (a) or torin 1 (b) treatment after 16 hr exposure. Data presented are averages from 5 to 6 independent experiments (mean ± SEM). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA and Dunnett's post hoc test. (c) Western blot showing the dose-dependent effects of torin 1 on Akt and S6 phosphorylation. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of torin for 16 hr. The last lane was the sample from cells treated with 20 nM rapamycin (Rapa) for 16 hr. (d) Immunofluorescence staining of TFEB nuclear translocation after 2 h exposure to 20 or 50 μM quercetin. Quantification data are presented in (e). Scale bar: 10 μm. (f) Measurement of TFEB nuclear translocation after subcellular fractionation. RPE cells were treated with 20 μM quercetin for 2 hr, and the amount of TFEB in the nuclear and cytosolic fractions was determined by Western blot analyses. Quantification data are presented in (g). Data presented are averages from 3 independent experiments (mean ± SEM). ∗p < 0.05. Student's t-test.