Figure 1.
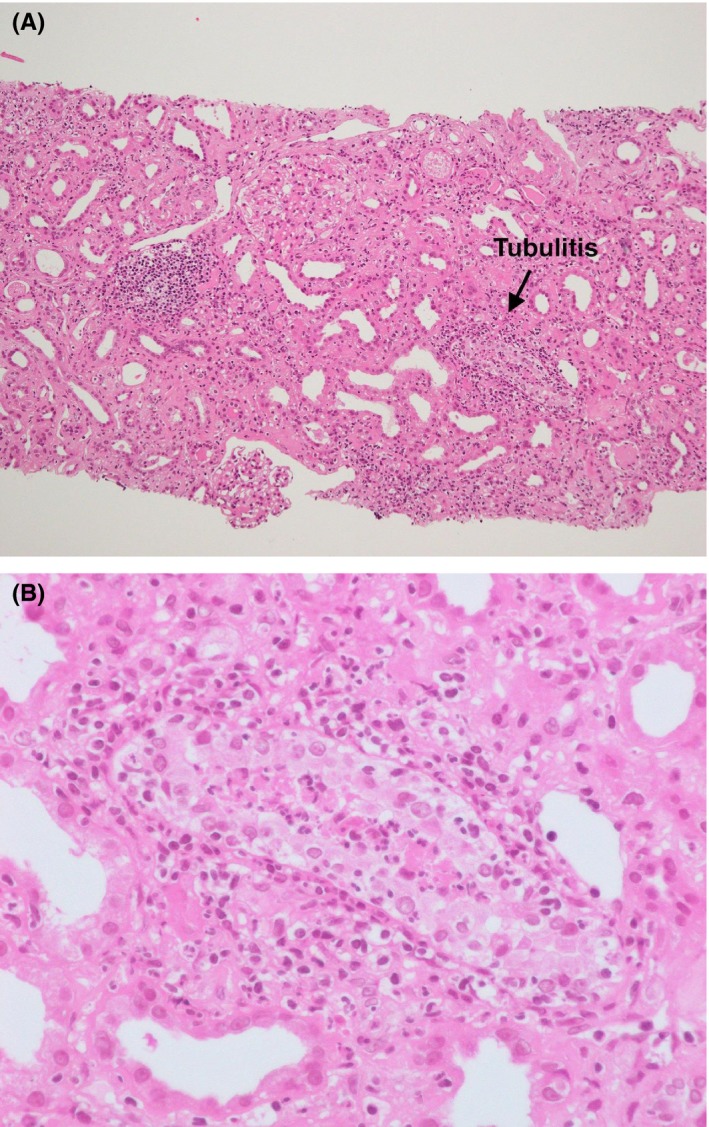
Pathology of acute interstitial nephritis. A, Hematoxylin and eosin staining. The glomeruli are mostly intact. On the other hand, tubulitis is shown and lymphocytes and plasma cells are invading the fibrosed tubulointerstitium (×100). B, The portion of tubulitis is enlarged (arrow, A). Neutrophils are infiltrating the tubules and tubular epithelial cells, most of which show degenerative changes
