Figure 3.
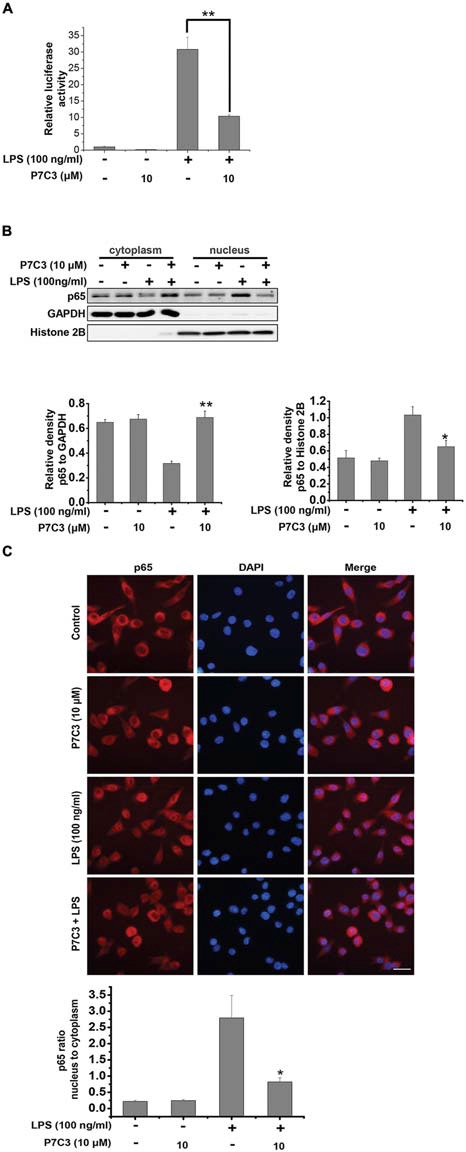
P7C3 inhibited LPS-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 subunit in BV2 cells. (A) The stable BV2 NF-κB reporter cells were pretreated with P7C3 (10 μM) for 2 h and then exposed to LPS (100 ng/mL) for 6 h. Then, the expressions of the NF-κB reporter gene were examined. Data from three independent experiments were presented as the means ± SEM. Mann and Whitney for comparison between groups, **P < 0.01. (B) BV2 cells were pretreated with P7C3 (10 μM) for 2 h and then exposed to LPS (100 ng/mL) for 15 min. After incubation, the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were separated using subcellular fractionation methods. The p65 protein levels in cytoplasm and nucleus were detected using immunoblot analysis. The quantitative analyses of the relative density of p65 to loading controls in cytoplasm (GAPDH) or in the nucleus (Histone 2B) were shown in the lower panels. The values were presented as the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. Mann and Whitney for comparison between groups, **P < 0.01 vs. the group treated with LPS. (C) BV2 cells that were treated as (B) were fixed and labeled with anti-p65 (red) antibodies. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (1 μg/mL; blue). The cells were then visualized using a fluorescent microscope. Scale bar, 10 μm. The ratio of nucleus to cytoplasm of p65 was quantified. The values are presented as the means ± SEM from three independent experiments. Kruskal–Wallis test followed by the Iman-Conover method for multiple comparison between groups was performed, *P < 0.05, vs. the group treated with LPS alone.
