Figure 8.
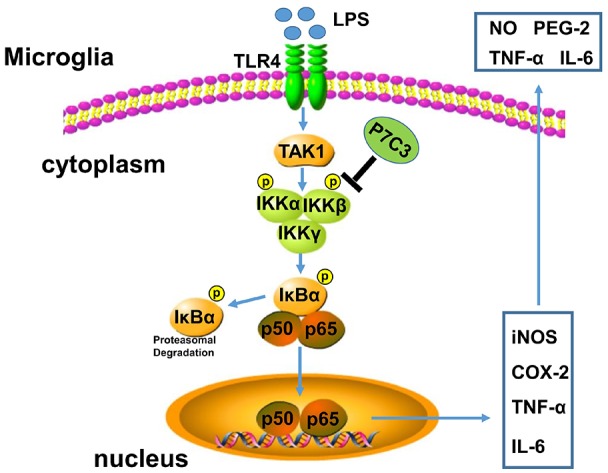
A schematic diagram shows the involvement of the IKK/IκBα/NF-κB pathway in P7C3-mediated repression of microglial activation. Once the Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) is activated via its exogenous ligand LPS, TAK1 could be recruited to TLR4 and be autophosphorylated. Phosphorylation of TAK1 leads to an activation of the IKK complex containing IKK-α, IKK-β and IKK-γ. The IKK complex phosphorylates IκBα, leading to its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation, which allows NF-κB translocation to nucleus and targets inflammatory gene expressions including iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6. However, a pretreatment of P7C3 inhibits IKK activation, thus, LPS-induced NF-κB activation is suppressed, leading a repression of inflammatory gene expressions.
