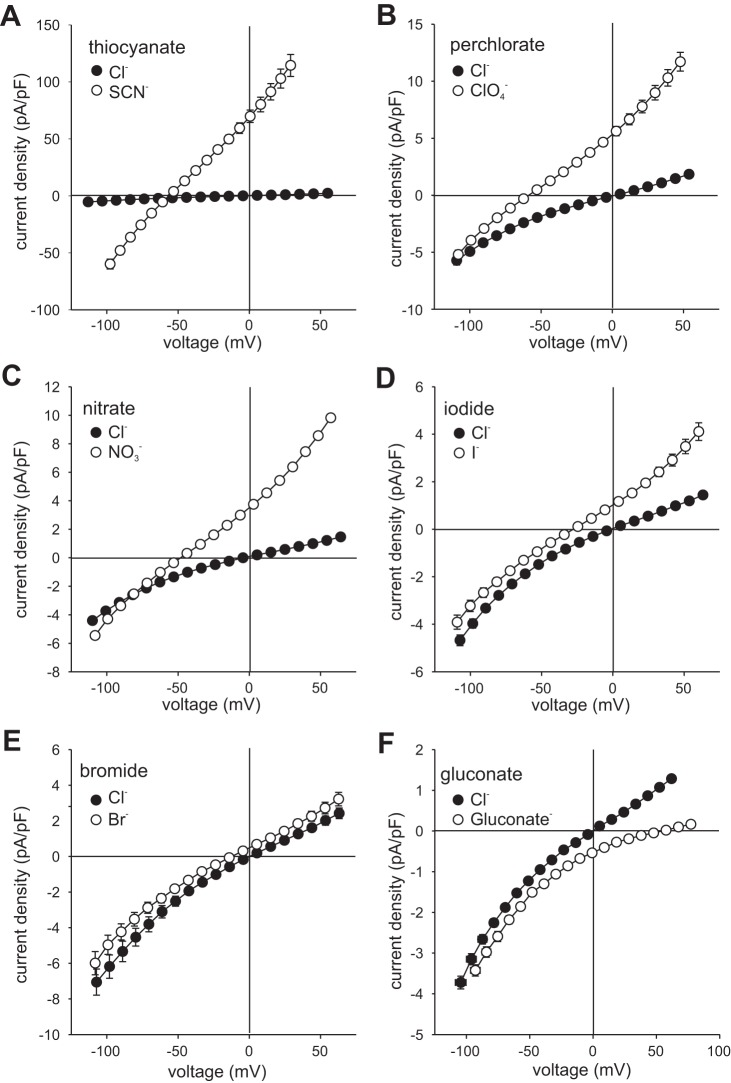
Fig. 2.
Effect of anion substitutions on the whole cell current-voltage (I-V) relationship. Cells were dialyzed with NMDG-Cl-based internal solution and currents were recorded before and after replacement of 140 mM external NaCl with NaSCN (A, n = 8) 140 mM NaClO4 (B, n = 9), NaNO3 (C, n = 20), NaI (D, n = 8), NaBr (E, n = 8), or Na-gluconate (F, n = 9). Currents in SCN− and ClO4− are instantaneous currents evoked by voltage steps; currents in all other anions were generated by 1-s voltage ramps from −120 to +60 mV. Holding potential was −60 mV. Mean reversal potential (Erev) values in the presence of Cl− and substitute anions are as follows: SCN−, −56.3 ± 0.8 mV (± SE, n = 8); ClO4−, −59.3 ± 1.6 mV (n = 10); , −48.0 ± 1.5 mV (n = 21); I−, −27.9 ± 3.3 mV (n = 8); Br−, −12.1 ± 1.9 mV (n = 9); Cl−, −0.9 ± 0.7 mV (n = 64); gluconate, +54.0 ± 2.3 mV (n = 9). Symbols represent mean current density, and bidirectional error bars represent SE; where not visible, the error bars are smaller than the symbols. Voltages are corrected for liquid junction potentials and the voltage drop across the series resistance.