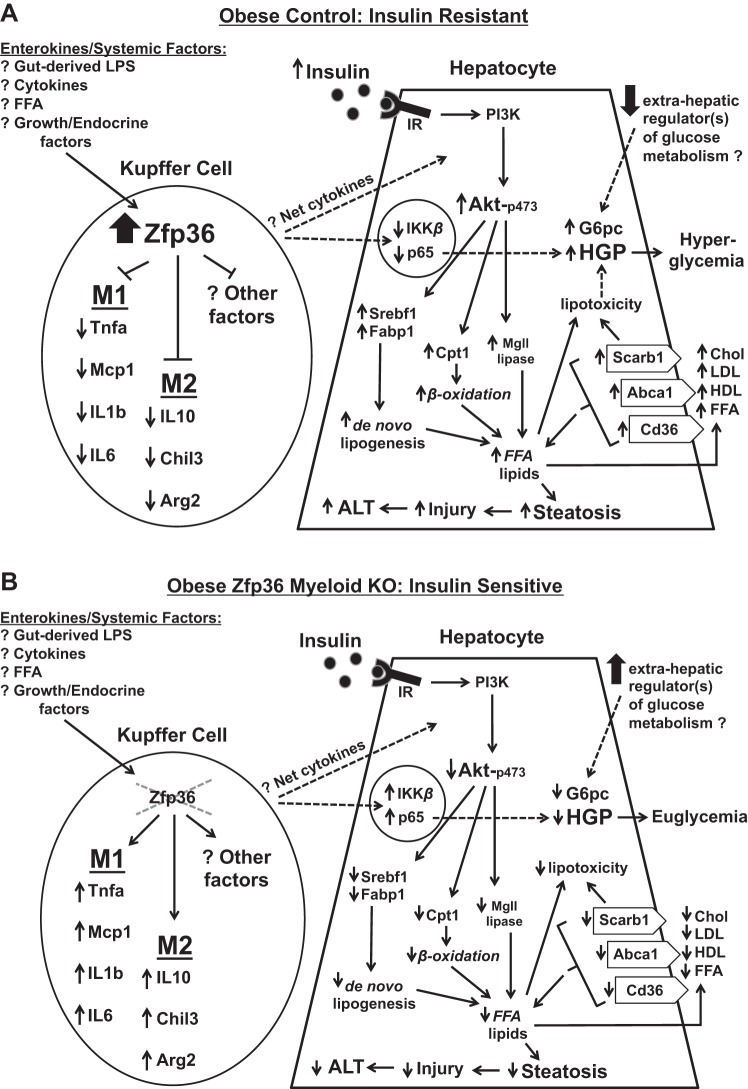
Fig. 11.
Model summarizing the effects of Kupffer-expressed zinc finger protein 36 (Zfp36) on the hepatic response to insulin in obese mice. Dotted lines indicate potential effects that remain to be fully explored. A: in obese Control (Zfp36fl/fl) mice, Zfp36 expression is upregulated in Kupffer cells (KC), leading to reduced expression of classically activated and alternatively activated (M1 and M2, respectively) cytokines. The factors that stimulate Zfp36 expression in the KCs of obese mice remain to be determined, but candidates include gut-derived endotoxin (LPS), as well as systemic or local lipids, cytokines, or growth factors that are perturbed in obese mice. The net effect of enhanced Zfp36 expression in KCs is to provoke insulin resistance in hepatocytes: this is demonstrated by the well-documented preservation of the lipid-promoting effects of insulin coupled with the impaired ability of insulin to regulate hepatic glucose production (HGP). The insulin-resistant mice experience hyperlipidemia, hepatic triglyceride (TG) accumulation/steatosis, and hyperglycemia. Extrahepatic factors responsible for modulating glucose metabolism in the livers of insulin-resistant mice may be impaired, although specific factors remain to be fully established (62). B: in obese, conditional Zfp36fl/fl;LysMCre [myeloid knockout (KO)] mice, loss of KC-expressed Zfp36 leads to enhanced expression of M1 and M2 cytokines. The net effects of these factors are to enhance insulin sensitivity in the livers of the KO mice; this is demonstrated by reduced lipid production and improved glucose tolerance in the KO mice. Improved insulin sensitivity in the KO mice leads to reduced hyperlipidemia, reduced hepatic TG accumulation/steatosis, and euglycemia. The improvement in insulin sensitivity is associated with enhanced activation of p65 in the livers of the KO mice, a feature recently described to contribute to the insulin response in the liver (32). FFA, free fatty acid; Mcp1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; Chil3, Chitinase-like 3; Arg2, arginase-2; IR, insulin receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; G6pc, glucose-6-phosphatase; Srebf1, sterol response element-binding factor 1; Fabp1, fatty acid-binding protein 1; Cpt1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; Mgl1, macrophage galactose-type lectin 1; Scarb1, scavenger receptor class B member 1; Abca1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1; Cd36, cluster of differentiation 36; Chol, cholesterol; ALT, alanine transaminase.