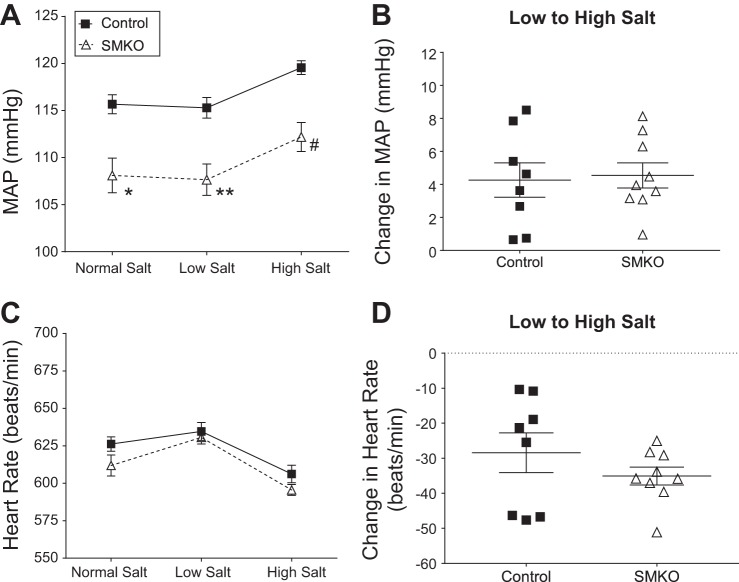
Fig. 1.
Type 1A angiotensin receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells contribute to basal blood pressure (BP), but not response to Na+. A: mean arterial pressure (MAP) in control (n = 8) and SMKO (n = 9) mice fed normal (0.4% Na+)-, low (0.02% Na+)-, and high (6% Na+)-salt diets over 5 days. Values are means ± SE. Data were analyzed by 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. ANOVA table for genotype: F(1,15) = 15.7, P < 0.001; Sidak’s post hoc test: *P = 0.002, **P = 0.001, #P = 0.002. B: Na+ sensitivity, measured as change in MAP from high- to low-salt diet, was not significantly different (by unpaired t-test) between control (n = 8) and SMKO (n = 9) mice. Values are means ± SE. C: heart rate, averaged over each of the 5-day periods of salt diet feeding (as described in A), in control (n = 8) and SMKO (n = 9) mice. Heart rates increased during low-salt feeding and decreased during high-salt feeding. There was no significant difference between groups. D: average change in heart rate from high- to low-salt diet was not significantly different (by unpaired t-test) between control (n = 8) and SMKO (n = 9) mice. Values are means ± SE.