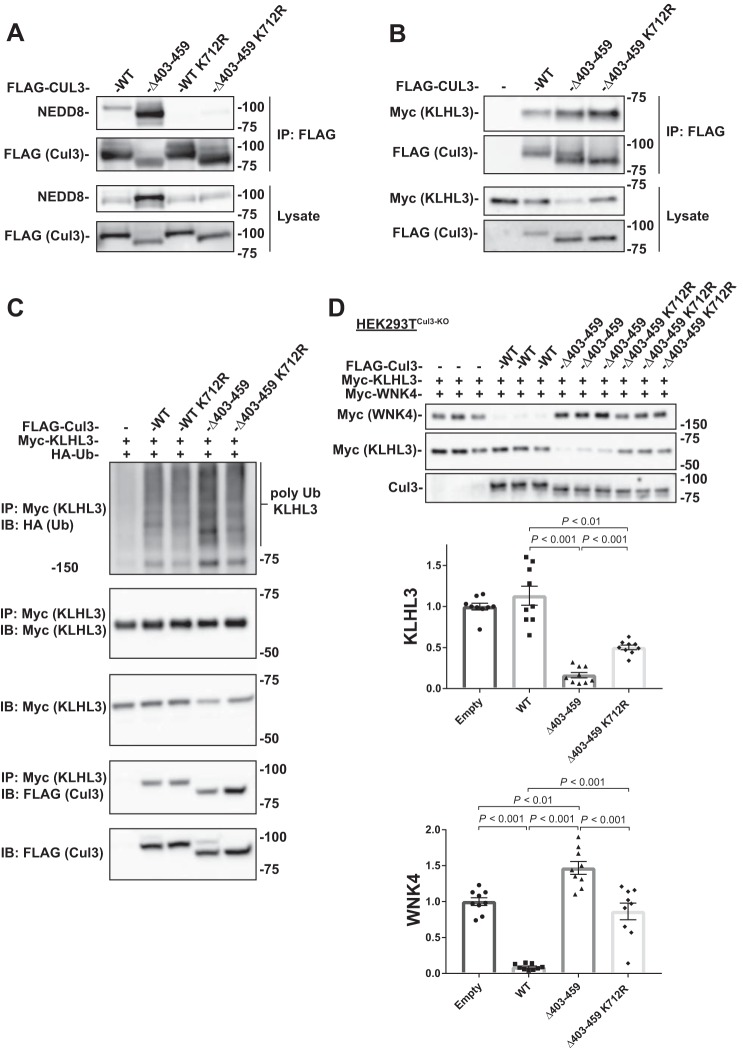
Fig. 4.
Ligase-deficient Cul3Δ403–459 K712R double mutant blunts the effects of Cul3Δ403–459 on KLHL3 and WNK4. A: FLAG-tagged Cul3 constructs were cotransfected into HEK293 cells and immunoprecipitated using FLAG antibody. Immunoblotting for NEDD8 showed no neddylation of the K712R mutant for both WT Cul3 and Cul3Δ403–459. B: Coimmunoprecipitation was performed with HEK293 cells transfected with myc-KLHL3 and FLAG-tagged WT Cul3, Cul3Δ403–459, Cul3Δ403–459 K712R, or empty vector. Pull-down with FLAG antibodies showed that KLHL3 had more binding to Cul3Δ403–459 and Cul3Δ403–459 K712R proteins. C: Ubiquitin assay was performed for KLHL3 in HEK293 cells by cotransfecting FLAG-tagged Cul3 constructs with myc-KLHL3 and HA-tagged ubiquitin. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-myc antibody and polyubiquitylation of KLHL3 was visualized by immunoblotting for anti-HA. Cul3Δ403–459 K712R double mutant attenuated the higher abundance of KLHL3 ubiquitylation shown with Cul3Δ403–459. D: Top, abundance of myc-tagged KLHL3 and WNK4 protein was examined by immunoblot in Cul3 knockdown HEK293T (HEK293TCul3-KO) cells cotransfected with different FLAG-tagged Cul3 constructs. KLHL3 and WNK4 expression was higher and lower, respectively, in Cul3Δ403–459 K712R compared with Cul3Δ403–459. Bottom, quantitative analysis of KLHL3 and WNK4 protein abundance. Stain-free imaging was used as a loading control. Data represent individual values as well as means ± SE relative to control. Statistical differences were examined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Cul3, cullin 3; HA, hemagglutinin; HEK, human embryonic kidney; IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation; KLHL3, kelch-like 3; Ub, ubiquitin; WNK, with-no-lysine kinase; WT, wild type.