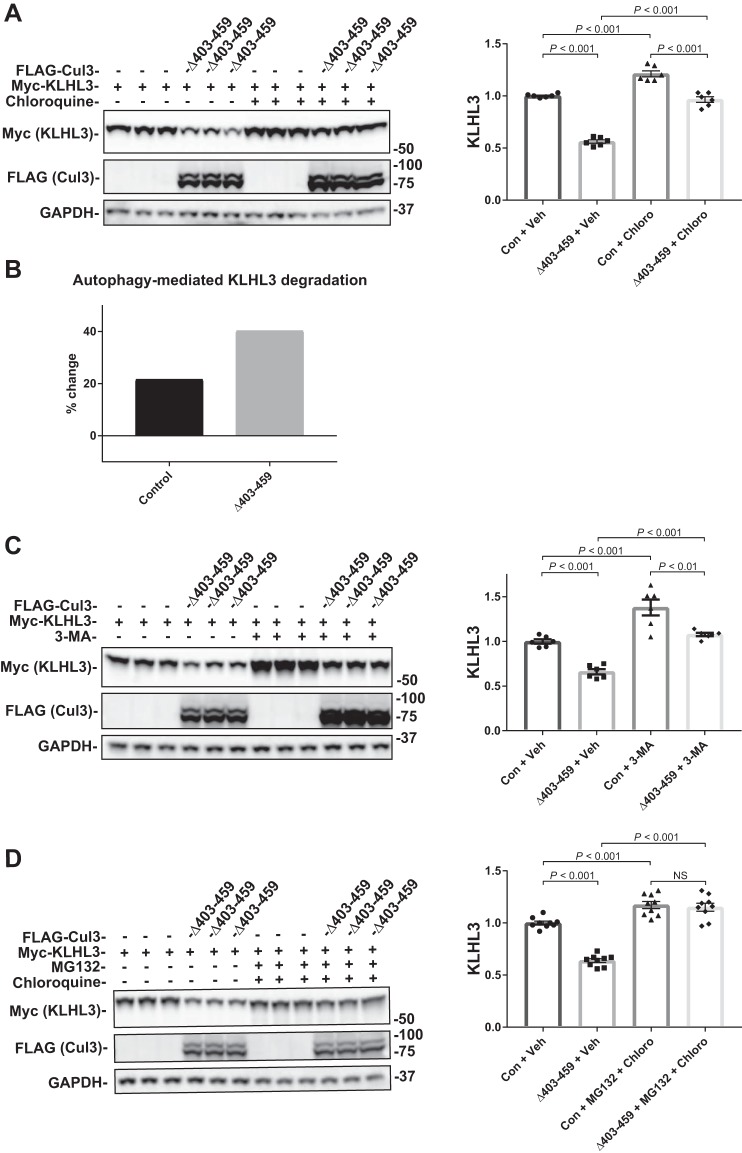
Fig. 6.
Effects of autophagy inhibition on Cul3Δ403–459-mediated KLHL3 degradation. The pathway for degradation of KLHL3 by the Cul3Δ403–459 mutant was examined by inhibiting the autophagy pathway with the drugs chloroquine or 3-methyladenine (3-MA). HEK293 cells were cotransfected with myc-KLHL3 and either no Cul3 or FLAG-Cul3Δ403–459. The cells were incubated with vehicle or 100 μM chloroquine (A) or 5 mM 3-MA (C) for 18 h before harvesting. Immunoblot analysis showed that inhibition of autophagy with chloroquine or 3-MA partially blocked Cul3Δ403–459-mediated KLHL3 degradation, whereas administration of the drugs together completely eliminated KLHL3 degradation. Right, quantitative analysis of KLHL3 protein abundance. B: Bar graph depicting the percent change in KLHL3 protein abundance caused by autophagy inhibition from chloroquine administration between control and Cul3Δ403–459 groups. D: HEK293 cells were incubated with both the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 and autophagy inhibitor chloroquine, simultaneously. Administration of the drugs together completely eliminated KLHL3 degradation. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Data represent individual values as well as means ± SE relative to control. Statistical differences were examined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Con, control; Cul3, cullin 3; HEK, human embryonic kidney; KLHL3, kelch-like 3; Veh, vehicle.